Modulation of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling by P2 purinergic receptors in human fetal astrocytes
- PMID: 10884313
- PMCID: PMC6772323
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-14-05292.2000
Modulation of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling by P2 purinergic receptors in human fetal astrocytes
Abstract
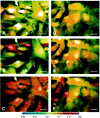
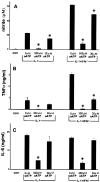
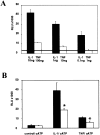
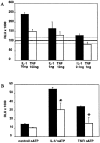
In human astrocytes, interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) is a potent inducer of genes associated with inflammation. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that in primary cultures of human fetal astrocytes signaling by the P2 purinergic nucleotide receptor pathway contributes to, or modulates, cytokine-mediated signal transduction. Calcium imaging studies indicated that most cells in culture responded to ATP, whereas only a subpopulation responded to UTP. Pretreatment of astrocytes with P2 receptor antagonists, including suramin and periodate oxidized ATP (oATP), resulted in a significant downregulation of IL-1beta-stimulated expression of nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor (TNFalpha), and IL-6 at both the protein and mRNA levels, without affecting cell viability. In cells transiently transfected with reporter constructs, IL-1beta demonstrated more potent activation of the transcription factors nuclear factor -kappaB (NF-kappaB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) than TNFalpha. However, pretreatment with oATP downregulated activation of NF-kappaB and AP-1 by IL-1beta or TNFalpha. Electromobility shift assays using oligonucleotides containing specific NF-kappaB binding sequences confirmed that pretreatment with oATP or apyrase attenuated cytokine-mediated induction of this transcription factor. From these data, we conclude that P2 receptor-mediated signaling intersects with that of IL-1beta and TNFalpha to regulate responses to cytokines in the CNS. Because inflammation, trauma, and stress all lead to the release of high levels of extracellular nucleotides, such as ATP and UTP, signaling via P2 receptors may provide a mechanism whereby cells can sense and respond to events occurring in the extracellular environment and can fine tune the transcription of genes involved in the inflammatory response.
Figures




References
-
- Breder CD, Dinarello CA, Saper CB. Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science. 1988;240:321–324. - PubMed
-
- Bruner G, Murphy S. Purinergic P2Y receptors on astrocytes are directly coupled to phospholipase A2. Glia. 1993;7:219–224. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. The past, present and future of purine nucleotides as signalling molecules. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1127–1139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
