Characterization of mercuric mercury (Hg2+)-induced lymphoblasts from patients with mercury allergy and from healthy subjects
- PMID: 10886235
- PMCID: PMC1905683
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01268.x
Characterization of mercuric mercury (Hg2+)-induced lymphoblasts from patients with mercury allergy and from healthy subjects
Abstract
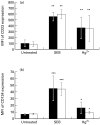
Hg2+ induces lymphocyte proliferation when added to cell cultures from both healthy and mercury-allergic subjects. Consequently, when measuring DNA synthesis a possible Hg2+-specific response, resulting from proliferating memory cells, cannot be discriminated from a non-allergic response. The mechanism behind this non-allergic response is unknown but a superantigenic effect of Hg2+ has been suggested. In this study, five mercury-allergic patients, with oral lichen planus (OLP) lesions adjacent to dental amalgam and a positive patch test to Hg0, and five healthy subjects without amalgam were examined. The immunophenotype and the T cell receptor Vbeta (TCR Vbeta) repertoire of Hg2+-induced lymphoblasts as well as the expression of the lymphocyte activation markers CD23 and CD134 were analysed for possible differences between healthy and allergic subjects. The mechanism of Hg2+-induced proliferation was examined by comparing the TCR Vbeta expression of Hg- and staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB)-activated lymphoblasts, the latter used as a positive superantigen control. It was not possible to discriminate between mercury-allergic and healthy subjects using the immunophenotype or the TCR Vbeta profile of the Hg2+-induced lymphoblasts or the expression of CD23 and CD134. However, Hg2+-induced CD4+ lymphoblasts showed a skewing towards Vbeta2. This relative increase in Vbeta2 was only detected in the CD4+ but not in the CD8+ lymphoblast population. In conclusion, Hg2+ induced a proliferation-dependent skewing towards CD4+ but not CD8+ lymphocytes expressing Vbeta2. In this respect Hg2+ differs from the classical bacterial superantigen SEB, which also stimulates unique TCR Vbeta families among CD8+ cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vitro lymphoproliferative assays with HgCl2 cannot identify patients with systemic symptoms attributed to dental amalgam.J Dent Res. 1999 Aug;78(8):1450-8. doi: 10.1177/00220345990780081101. J Dent Res. 1999. PMID: 10439033
-
HgCl(2)-induced human lymphocyte activation in vitro: a superantigenic mechanism?Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999 Sep;120(1):63-70. doi: 10.1159/000024221. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10529590
-
Cytokine production, lymphocyte proliferation and T-cell receptor Vbeta expression in primary peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures from nickel-allergic individuals.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003 Dec;132(4):373-9. doi: 10.1159/000074905. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14707469
-
Characterization of primary recall in vitro lymphocyte responses to bacampicillin in allergic subjects.Clin Exp Allergy. 2000 Oct;30(10):1450-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2000.00905.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000. PMID: 10998023
-
Lymphocyte-based model systems for allergy research: a historic overview.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014;163(4):259-91. doi: 10.1159/000360163. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24777172 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Diagnosis and Management of Allergic Reactions Caused by Chinese Materia Medica.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022 Feb;62(1):103-122. doi: 10.1007/s12016-020-08812-7. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 33606192 Review.
-
The Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Pruritus Mechanisms of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 2;12:735295. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.735295. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34925005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolewska J, Hansen HJ, Holmstrup P, Pindborg JJ, Stangerup M. Kontaktlæsioner i mundslimhinden ved korroderende dentale solvamalgamrestaureringer. Tandlægebladet. 1986;90:613–26. - PubMed
-
- James J, Ferguson MM, Forsyth A, Tulloch N, Lamey PJ. Oral lichenoid reactions related to mercury sensitivity. Br J Maxillofac Surg. 1987;25:474–80. - PubMed
-
- Holmstrup P. Oral mucosa and skin reactions related to amalgam. Adv Dent Res. 1992;6:120–4. - PubMed
-
- Nyfeler B, Pichler WJ. The lymphocyte transformation test for the diagnosis of drug allergy: sensitivity and specificity. Clin Exp Allergy. 1997;27:175–81. - PubMed
-
- Von Blomberg-van der Vlier BME, Bruynzeel DP, Scheper RJ. Impact of 25 years of in vitro testing in allergic contact dermatitis. In: Frosch PJ, Dooms-Goossens A, Lachapelle J-M, Rycroft RJG, Scheper RJ, editors. Current topics in dermatitis. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag; 1989. pp. 569–77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

