Levamisole induces interleukin-18 and shifts type 1/type 2 cytokine balance
- PMID: 10886398
- PMCID: PMC2327010
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00042.x
Levamisole induces interleukin-18 and shifts type 1/type 2 cytokine balance
Abstract
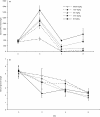
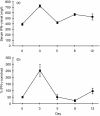
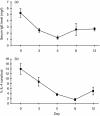
Immune responses can be classified, according to the predominant cytokines involved, into type 1 (featuring interferon-gamma, IFN-gamma) and type 2 (featuring interleukin-4, IL-4); imbalance between type 1 and type 2 cytokine compartments has been implicated in many human diseases. Levamisole is a drug with an unknown mode of action that has been used to boost immunity in infectious diseases including leprosy, and in some cancers. To test the hypothesis that levamisole acts by inducing a shift to a type 1 immune response, we used Brown Norway (BN) rats, which are markedly biased to type 2 responses. BN rats treated with levamisole showed a dose-dependent rise in serum IFN-gamma and fall in serum immunoglobulin E (IgE) level. Detailed analysis of cytokine gene expression showed upregulation of IFN-gamma and downregulation of IL-4 messenger RNA. This coincided with marked upregulation of IL-18, a recently characterized cytokine with potent activity in stimulating IFN-gamma production. IL-12 was not induced. Further, the type 2 response induced in BN rats by mercuric chloride was markedly attenuated when rats were pretreated with levamisole: there was a 2-log reduction in maximum serum IgE level and marked attenuation of IL-4 gene upregulation. These data indicate that levamisole acts by resetting the immune balance towards a type 1 response via induction of IL-18. Our findings provide a direction for development of more specific immunomodulating therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145. - PubMed
-
- Bloom BR, Modlin RL, Salgame P. Stigma variations: observations on supppressor T cells and leprosy. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:453. - PubMed
-
- Heurtier AH, Boitard C. T-cell regulation in murine and human autoimmune diabetes: the role of TH1 and TH2 cells. Diabetes Metab. 1997;23:377. - PubMed
-
- Cohen IR. The Th1/Th2 dichotomy, hsp60 autoimmunity, and type I diabetes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997;84:103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

