Cooperative effects of genes controlling the G(2)/M checkpoint
- PMID: 10887152
- PMCID: PMC316737
Cooperative effects of genes controlling the G(2)/M checkpoint
Abstract
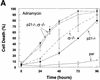
It is believed that multiple effectors independently control the checkpoints permitting transitions between cell cycle phases. However, this has not been rigorously demonstrated in mammalian cells. The p53-induced genes p21 and 14-3-3sigma are each required for the G(2) arrest and allow a specific test of this fundamental tenet. We generated human cells deficient in both p21 and 14-3-3sigma and determined whether the double knockout was more sensitive to DNA damage than either single knockout. p21(-/-) 14-3-3sigma(-/-) cells were significantly more sensitive to DNA damage or to the exogenous expression of p53 than cells lacking only p21 or only 14-3-3sigma. Thus, p21 and 14-3-3sigma play distinct but complementary roles in the G(2)/M checkpoint, and help explain why genes at the nodal points of growth arrest pathways, like p53, are the targets of mutation in cancer cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
14-3-3sigma is a p53-regulated inhibitor of G2/M progression.Mol Cell. 1997 Dec;1(1):3-11. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80002-7. Mol Cell. 1997. PMID: 9659898
-
Neither p21WAF1 nor 14-3-3sigma prevents G2 progression to mitotic catastrophe in human colon carcinoma cells after DNA damage, but p21WAF1 induces stable G1 arrest in resulting tetraploid cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Oct 15;61(20):7660-8. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11606409
-
Dissociation between cell cycle arrest and apoptosis can occur in Li-Fraumeni cells heterozygous for p53 gene mutations.Oncogene. 1997 May 8;14(18):2137-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201050. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9174049
-
Regulation of the G2/M transition by p53.Oncogene. 2001 Apr 5;20(15):1803-15. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204252. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11313928 Review.
-
[Cell cycle regulation after exposure to ionizing radiation].Bull Cancer. 1999 Apr;86(4):345-57. Bull Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10341340 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Phosphorylation of p21 in G2/M promotes cyclin B-Cdc2 kinase activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;25(8):3364-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.8.3364-3387.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15798220 Free PMC article.
-
Interference with energy metabolism by 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside induces HPV suppression in cervical carcinoma cells and apoptosis in the absence of LKB1.Biochem J. 2007 May 1;403(3):501-10. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061053. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17212587 Free PMC article.
-
The radiation response of androgen-refractory prostate cancer cell line C4-2 derived from androgen-sensitive cell line LNCaP.Asian J Androl. 2010 May;12(3):405-14. doi: 10.1038/aja.2009.91. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Asian J Androl. 2010. PMID: 20118949 Free PMC article.
-
Stable low-level expression of p21WAF1/CIP1 in A549 human bronchogenic carcinoma cell line-derived clones down-regulates E2F1 mRNA and restores cell proliferation control.Mol Cancer. 2006 Jan 10;5:1. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-5-1. Mol Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16403226 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT-1) role in ovarian cancer progression-An in vitro study.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0228024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228024. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31978092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon JI, Beach D, Jacks T, Hannon GJ. Radiation-induced cell arrest compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 1995;377:552–557. - PubMed
-
- Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown JP, Sedivy JM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science. 1998;282:1497–1501. - PubMed
-
- Cahill DP, Lengauer C, Yu J, Riggins GJ, Willson JK, Markowitz SD, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Mutations of mitotic checkpoint genes in human cancers. Nature. 1998;392:300–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
