DNA vaccines encoding viral glycoproteins induce nonspecific immunity and Mx protein synthesis in fish
- PMID: 10888644
- PMCID: PMC112222
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.15.7048-7054.2000
DNA vaccines encoding viral glycoproteins induce nonspecific immunity and Mx protein synthesis in fish
Abstract
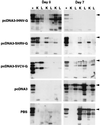
Protective immunity by vaccination with plasmid DNA encoding a viral glycoprotein (G) has long been assumed to result from the induction of a specific immune response. We report here that the initial protection may be due to the induction of alpha/beta interferon, with long-term protection due to a specific response to the encoded viral G. DNA vaccines encoding the Gs of three serologically unrelated fish rhabdoviruses were used to vaccinate rainbow trout against a lethal challenge with infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV). All three vaccines, each encoding the G gene of either IHNV (IHNV-G), snakehead rhabdovirus (SHRV) (SHRV-G), or spring viremia of carp virus (SVCV) (SVCV-G), elicited protective immunity against IHNV. Vaccinated fish were challenged at 30 or 70 days postvaccination with lethal doses of IHNV. At 30 days postvaccination, only 5% of fish that had received any of the G vaccines died, whereas more than 50% of the control fish succumbed to virus challenge. When fish were vaccinated and challenged at 70 days postvaccination, only 12% of the IHNV-G-vaccinated fish died compared to 68% for the SHRV-G- and 76% for the SVCV-G-vaccinated fish. Assays for trout Mx protein, an indicator of alpha/beta interferon induction, showed that only fish vaccinated with a G-containing plasmid produced high levels of Mx protein in the kidneys and liver. Interestingly, at day 7 after virus challenge, all of the fish vaccinated with the IHNV-G plasmid were negative for Mx, but the SHRV-G- and SVCV-G-vaccinated fish still showed detectable levels of Mx. These results suggest that DNA vaccines in fish induce an early, nonspecific antiviral protection mediated by an alpha/beta interferon and, later, a specific immune response.
Figures

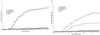

Similar articles
-
An oral DNA vaccine against infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) encapsulated in alginate microspheres induces dose-dependent immune responses and significant protection in rainbow trout (Oncorrhynchus mykiss).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Aug;45(2):877-88. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.05.045. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26054788
-
Evaluation of the protective immunogenicity of the N, P, M, NV and G proteins of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus in rainbow trout oncorhynchus mykiss using DNA vaccines.Dis Aquat Organ. 1999 Dec 22;39(1):29-36. doi: 10.3354/dao039029. Dis Aquat Organ. 1999. PMID: 11407402
-
Immunogenicity of a recombinant infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus glycoprotein produced in insect cells.Dis Aquat Organ. 1999 Apr 15;36(1):67-72. doi: 10.3354/dao036067. Dis Aquat Organ. 1999. PMID: 10349553
-
DNA vaccines as a tool for analysing the protective immune response against rhabdoviruses in rainbow trout.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002 May;12(5):439-53. doi: 10.1006/fsim.2002.0422. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12194454 Review.
-
Reverse genetics on fish rhabdoviruses: tools to study the pathogenesis of fish rhabdoviruses.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;292:119-41. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27485-5_6. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15981470 Review.
Cited by
-
Fundamentals of Fish Vaccination.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2411:147-173. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1888-2_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34816404
-
Effects of different cytokines on immune responses of rainbow trout in a virus DNA vaccination model.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 11;8(68):112222-112235. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23095. eCollection 2017 Dec 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29348820 Free PMC article.
-
Introduction of translation stop codons into the viral glycoprotein gene in a fish DNA vaccine eliminates induction of protective immunity.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2006 Jul-Aug;8(4):351-6. doi: 10.1007/s10126-005-5154-6. Epub 2006 Jun 12. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2006. PMID: 16761198
-
Heterologous DNA prime-protein boost immunization with RecA and FliD offers cross-clade protection against leptospiral infection.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 24;8(1):6447. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24674-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29691454 Free PMC article.
-
IRF9-Stat2 Fusion Protein as an Innate Immune Inducer to Activate Mx and Interferon-Stimulated Gene Expression in Zebrafish Larvae.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017 Jun;19(3):310-319. doi: 10.1007/s10126-017-9752-x. Epub 2017 May 12. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2017. PMID: 28500614
References
-
- Anderson E D, Mourich D V, Fahrenkrug S C, LaPatra S, Shepherd J, Leong J C. Genetic immunization of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) against infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol. 1996;5:114–122. - PubMed
-
- Bazzigher L, Schwarz A, Staeheli P. No enhanced influenza virus resistance of murine and avian cells expressing cloned duck Mx protein. Virology. 1993;195:100–112. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi D, Schultz U, Staeheli P. The interferon-induced Mx protein of chickens lacks antiviral activity. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995;15:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Bjorklund H V, Higman K H, Kurath G. The glycoprotein genes and gene junctions of the fish rhabdoviruses spring viremia of carp virus and hirame rhabdovirus: analysis of relationships with other rhabdoviruses. Virus Res. 1996;42:65–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

