Autozygosity mapping of a seckel syndrome locus to chromosome 3q22. 1-q24
- PMID: 10889046
- PMCID: PMC1287195
- DOI: 10.1086/303023
Autozygosity mapping of a seckel syndrome locus to chromosome 3q22. 1-q24
Abstract
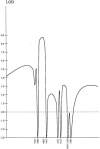
Seckel syndrome (MIM 210600) is an autosomal recessive disorder of low birth weight, severe microcephaly, and dysmorphic facial appearance with receding forehead, prominent nose, and micrognathia. We have performed a genomic screen in two consanguineous families of Pakistani origin and found that the disorder segregates with markers between loci D3S1316 and D3S3710, which map to chromosome 3q22.1-q24. Analysis using HOMOZ/MAPMAKER gave a maximum LOD score of 8.72. All five affected individuals were homozygous for the same allele, for two adjacent polymorphic markers within the region segregating with the disease, narrowing the region to 12 cM.
Figures
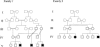

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for Seckel syndrome [MIM 210600], AT [MIM 208900], NBS [MIM 251260], and BLM [MIM 210900])
-
- Unified Database for Human Genome Mapping, The http://bioinformatics.weizmann.ac.il/udb (for markers)
References
-
- Bass H, Smith L, Sparkes R, Gycpes M (1975) Case report 33. Syndrome Ident 3:12–14
-
- Carney JP, Maser RS, Olivares H, Davis EM, Le Beau M, Yates JR III, Hays L, et al (1998) The hMre11/hRad50 protein complex and Nijmegen breakage syndrome: linkage of double-strand break repair to the cellular DNA damage response. Cell 93:477–486 - PubMed
-
- Cortez D, Wang Y, Qin J, Elledge SJ (1999) Requirement of ATM-dependent phosphorylation of brca1 in the DNA damage response to double-strand breaks. Science 286:1162–1166 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

