Cognitive-behavioral coping-skills therapy for alcohol dependence. Current status and future directions
- PMID: 10890800
- PMCID: PMC6760421
Cognitive-behavioral coping-skills therapy for alcohol dependence. Current status and future directions
Abstract
Cognitive-behavioral coping-skills training (CBST) is an alcoholism treatment approach aimed at improving the patients' cognitive and behavioral skills for changing their drinking behavior. CBST encompasses a variety of approaches that despite their core similarities differ in duration, modality, content, and treatment setting. Numerous studies and reviews have ranked CBST among the most effective approaches for treating alcoholic patients. Nevertheless, a recent analysis of nine studies failed to identify specific CBST components that could account for the treatment's effectiveness. Furthermore, a similar analysis of 26 studies suggested that CBST's superior effectiveness was limited to specific treatment contexts (i.e., when delivered as part of a comprehensive treatment program) and to specific patient subgroups (e.g., patients with less severe alcohol dependence). Several measures may help broaden CBST's focus and effectiveness, such as incorporating components of other treatment approaches.
Figures
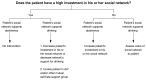
References
-
- Abrams DB, Niaura RS. Social learning theory. In: Blanke HT, Leonard KE, editors. Psychological Theories of Drinking and Alcoholism. New York: Guilford Press; 1987. pp. 131–178.
-
- Bandura A. Social Foundations of Thought and Action. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1986.
-
- Brown JM, Miller WR. Impact of motivational interviewing on participation in residential alcoholism treatment. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors. 1993;7:211–218.
-
- Chaney EF, O’Leary MR, Marlatt GA. Skill training with alcoholics. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 1978;46:1092–1104. - PubMed
-
- Finney JW, Monahan SC. The cost-effectiveness of treatment for alcoholism: A second approximation. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1996;57:229–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
