Role of the IkappaB kinase complex in oncogenic Ras- and Raf-mediated transformation of rat liver epithelial cells
- PMID: 10891479
- PMCID: PMC85990
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.15.5381-5391.2000
Role of the IkappaB kinase complex in oncogenic Ras- and Raf-mediated transformation of rat liver epithelial cells
Abstract
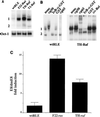
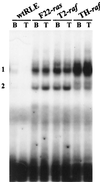
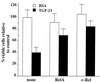
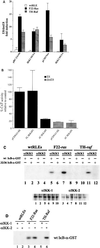
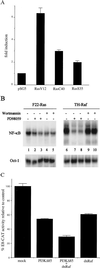
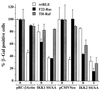
NF-kappaB/Rel factors have been implicated in the regulation of liver cell death during development, after partial hepatectomy, and in hepatocytes in culture. Rat liver epithelial cells (RLEs) display many biochemical and ultrastructural characteristics of oval cells, which are multipotent cells that can differentiate into mature hepatocytes. While untransformed RLEs undergo growth arrest and apoptosis in response to transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) treatment, oncogenic Ras- or Raf-transformed RLEs are insensitive to TGF-beta1-mediated growth arrest. Here we have tested the hypothesis that Ras- or Raf-transformed RLEs have altered NF-kappaB regulation, leading to this resistance to TGF-beta1. We show that classical NF-kappaB is aberrantly activated in Ras- or Raf-transformed RLEs, due to increased phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaB-alpha protein. Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity with a dominant negative form of IkappaB-alpha restored TGF-beta1-mediated cell killing of transformed RLEs. IKK activity mediates this hyperphosphorylation of IkappaB-alpha protein. As judged by kinase assays and transfection of dominant negative IKK-1 and IKK-2 expression vectors, NF-kappaB activation by Ras appeared to be mediated by both IKK-1 and IKK-2, while Raf-induced NF-kappaB activation was mediated by IKK-2. NF-kappaB activation in the Ras-transformed cells was mediated by both the Raf and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways, while in the Raf-transformed cells, NF-kappaB induction was mediated by the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Last, inhibition of either IKK-1 or IKK-2 reduced focus-forming activity in Ras-transformed RLEs. Overall, these studies elucidate a mechanism that contributes to the process of transformation of liver cells by oncogene Ras and Raf through the IkappaB kinase complex leading to constitutive activation of NF-kappaB.
Figures




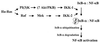
References
-
- Arsura M, FitzGerald M J, Fausto N, Sonenshein G E. NF-κB/Rel blocks transforming growth factor-β1-induced apoptosis of murine hepatocyte cell lines. Cell Growth Differ. 1997;8:1049–1059. - PubMed
-
- Arsura M, Wu M, Sonenshein G E. TGF-β1 inhibits NF-κB/Rel activity inducing apoptosis of B cells: transcriptional activation of IκB-α. Immunity. 1996;5:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P A, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin A S., Jr The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
