Evidence that dynamin-2 functions as a signal-transducing GTPase
- PMID: 10893263
- PMCID: PMC2185575
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.1.145
Evidence that dynamin-2 functions as a signal-transducing GTPase
Abstract
The role of dynamin GTPases in the regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis is well established. Here, we present new evidence that the ubiquitously expressed isoform dynamin-2 (dyn2) can also function in a signal transduction pathway(s). A </=5-fold increase of dyn2 relative to endogenous levels activates the transcription factor p53 and induces apoptosis, as demonstrated by reduced cell proliferation, DNA fragmentation, and caspase-3 activation. Dyn2-triggered apoptosis occurs only in dividing cells and is p53 dependent. A mutant defective in GTP binding does not trigger apoptosis, indicating that increased levels of dyn2.GTP, rather than protein levels per se, are required to transduce signals that activate p53. A truncated dyn2 lacking the COOH-terminal proline/arginine-rich domain (PRD), which interacts with many SH3 domain-containing partners implicated in both endocytosis and signal transduction, triggers apoptosis even more potently than the wild-type. This observation provides additional support for the importance of the NH(2)-terminal GTPase domain for the apoptotic phenotype. All described effects are dyn2-specific because >200-fold overexpression of dyn1, the 70% identical neuronal isoform, has no effect. Our data suggest that dyn2 can act as a signal transducing GTPase affecting transcriptional regulation.
Figures



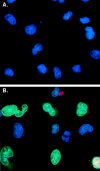






References
-
- Ahn S., Maudsley S., Luttrell L.M., Lefkowitz R.J., Daaka Y. Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of dynamin is required for beta2-adrenergic receptor internalization and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:1185–1188. - PubMed
-
- Behl C., Davis J.B., Lesley R., Schubert D. Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid beta protein toxicity. Cell. 1994;77:817–827. - PubMed
-
- Blagosklonny M.V. Loss of function and p53 protein stabilization. Oncogene. 1997;15:1889–1893. - PubMed
-
- Budihardjo I., Holt O., Lutter M., Luo X., Wang X. Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999;15:269–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

