Intracellular pH regulation by Na(+)/H(+) exchange requires phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
- PMID: 10893269
- PMCID: PMC2185553
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.1.213
Intracellular pH regulation by Na(+)/H(+) exchange requires phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
Abstract
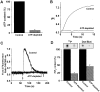
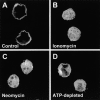
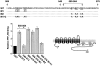
The carrier-mediated, electroneutral exchange of Na(+) for H(+) across the plasma membrane does not directly consume metabolic energy. Nevertheless, acute depletion of cellular ATP markedly decreases transport. We analyzed the possible involvement of polyphosphoinositides in the metabolic regulation of NHE1, the ubiquitous isoform of the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger. Depletion of ATP was accompanied by a marked reduction of plasmalemmal phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)) content. Moreover, sequestration or hydrolysis of plasmalemmal PIP(2), in the absence of ATP depletion, was associated with profound inhibition of NHE1 activity. Examination of the primary structure of the COOH-terminal domain of NHE1 revealed two potential PIP(2)-binding motifs. Fusion proteins encoding these motifs bound PIP(2) in vitro. When transfected into antiport-deficient cells, mutant forms of NHE1 lacking the putative PIP(2)-binding domains had greatly reduced transport capability, implying that association with PIP(2) is required for optimal activity. These findings suggest that NHE1 activity is modulated by phosphoinositides and that the inhibitory effect of ATP depletion may be attributable, at least in part, to the accompanying net dephosphorylation of PIP(2).
Figures

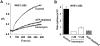
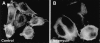


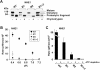
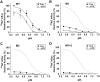
References
-
- Aharonovitz O., Grinstein S. Na+/H+ exchangersstructure, function and regulation. Drugs News Perspect. 1999;12:105–109.
-
- Aharonovitz O., Demaurex N., Woodside M., Grinstein S. ATP dependence is not an intrinsic property of Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1requirement for an ancillary factor. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;276:C1303–C1311. - PubMed
-
- Baukrowitz T., Schulte U., Oliver D., Herlitze S., Krauter T., Tucker S.J., Ruppersberg J.P., Fakler B. PIP2 and PIP as determinants for ATP inhibition of KATP channels. Science. 1998;282:1141–1144. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand B., Wakabayashi S., Ikeda T., Pouyssegur J., Shigekawa M. The Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 (NHE1) is a novel member of the calmodulin-binding proteins. Identification and characterization of calmodulin-binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:13703–13709. - PubMed
-
- Brown S.E., Heming T.A., Benedict C.R., Bidani A. ATP-sensitive Na+-H+ antiport in type II alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1991;261:C954–C963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

