All classes of calcium channel couple with equal efficiency to exocytosis in rat melanotropes, inducing linear stimulus-secretion coupling
- PMID: 10896721
- PMCID: PMC2270011
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00327.x
All classes of calcium channel couple with equal efficiency to exocytosis in rat melanotropes, inducing linear stimulus-secretion coupling
Abstract
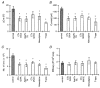
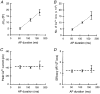
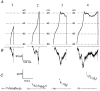
1. The contribution of low voltage-activated (LVA) T-type Ca2+ channels and four different types of high voltage-activated (HVA) Ca2+ channel to exocytosis, and the relationship between calcium influx and exocytosis during action potentials (APs) were studied in pituitary melanotropes. 2. Selective HVA Ca2+ channel blockers reduced exocytosis, monitored by membrane capacitance measurements, proportional to the reduction in Ca2+ influx. The efficacy of Ca2+ in stimulating exocytosis did not change in the presence of the Ca2+ channel blockers, indicating that all HVA Ca2+ channels act together in stimulating exocytosis. 3. The relationship between Ca2+ influx and exocytosis during the AP was examined using APs recorded from spontaneously active melanotropes as command templates under voltage clamp. Under voltage clamp, multiphasic Ca2+ currents were activated over the entire duration of the APs, i.e. during the rising phase as well as the plateau phase. The maximum amplitude of the Ca2+ current coincided with the peak of the AP. 4. The relationship between Ca2+ entry and exocytosis was linear for the different phases of the AP. Also, the influx of Ca2+ through LVA T-type channels stimulated exocytosis with the same efficacy as through the HVA channels. 5. APs of increasing duration ( approximately 50 to approximately 300 ms) evoked increasing amounts of exocytosis. The number of entering Ca2+ ions and the capacitance change were linearly related to AP duration, resulting in a fixed relationship between Ca2+ entry and exocytosis. 6. The results show that Ca2+ ions, entering a melanotrope, couple with equal strength to exocytosis regardless of the channel type involved. We suggest that the linear relationship between Ca2+ entry and secretion observed under physiological conditions (during APs), results from the equal strength with which LVA and HVA channels in melanotropes couple to exocytosis. This guarantees that secretion takes place over the entire duration of the AP.
Figures

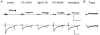


Similar articles
-
Dopamine modulates exocytosis independent of Ca(2+) entry in melanotropic cells.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Feb;87(2):793-801. doi: 10.1152/jn.00468.2001. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11826047
-
Melanotrope cells of Xenopus laevis express multiple types of high-voltage-activated Ca2+ channels.J Neuroendocrinol. 2005 Jan;17(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2005.01267.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15720469
-
Calcium current subtypes in GnRH neurons.Biol Reprod. 2003 Dec;69(6):1914-22. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.019265. Epub 2003 Aug 6. Biol Reprod. 2003. PMID: 12904316
-
Action of Ca2+ agonists/antagonists in mammalian peripheral neurons.Cell Biol Int Rep. 1989 Dec;13(12):1155-64. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(89)90029-5. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1989. PMID: 2561466 Review.
-
Molecular pharmacology of voltage-dependent calcium channels.Jpn J Pharmacol. 1996 Oct;72(2):83-109. doi: 10.1254/jjp.72.83. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8912911 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Ca v 3.1 channels by glucocorticoids.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Dec;29(8):1265-73. doi: 10.1007/s10571-009-9422-2. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19533336 Free PMC article.
-
T-type channels-secretion coupling: evidence for a fast low-threshold exocytosis.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Dec;453(3):373-83. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0100-7. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16758226 Review.
-
Otoferlin is critical for a highly sensitive and linear calcium-dependent exocytosis at vestibular hair cell ribbon synapses.J Neurosci. 2009 Aug 26;29(34):10474-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1009-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19710301 Free PMC article.
-
On depolarization-evoked exocytosis as a function of calcium entry: possibilities and pitfalls.Biophys J. 2011 Aug 17;101(4):793-802. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.06.061. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21843469 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen upregulates T-type calcium channels in the hypothalamus and pituitary.J Neurosci. 2006 Oct 25;26(43):11072-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3229-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17065449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ämmälä C, Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P. Calcium-independent potentiation of insulin release by cyclic AMP in single β cells. Nature. 1993;363:356–358. - PubMed
-
- Artalejo CR, Adams ME, Fox AP. Three types of Ca2+ channel trigger secretion with different efficacies in chromaffin cells. Nature. 1994;367:72–76. - PubMed
-
- Artalejo CR, Mogul DJ, Perlman RL, Fox AP. Bovine chromaffin cells exhibit three types of calcium channels: facilitation, induced by large pre-depolarizations or repetitive activity is due to the increased opening probability of a 27 pS channel. The Journal of Physiology. 1991;444:213–240. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

