A population pharmacokinetic analysis of the penetration of the prostate by levofloxacin
- PMID: 10898674
- PMCID: PMC90012
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.8.2046-2051.2000
A population pharmacokinetic analysis of the penetration of the prostate by levofloxacin
Abstract
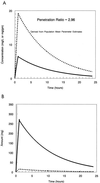
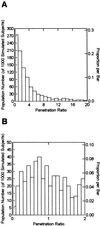
Prostatitis has remained a pathological entity that is difficult to treat. Part of the difficulty revolves about the putative offending pathogens. For acute prostatitis, members of the Enterobacteriaceae, particularly Escherichia coli, play a central role, while intracellular pathogens such as Chlamydia are more frequently seen in chronic prostatitis. Consequently, a drug needs to be able to penetrate to this specialized site in both the acute and chronic infection forms of the disease and also have potent activity against the most common causative pathogens, both intracellular and extracellular. Levofloxacin has such an activity profile. We wished to document its ability to penetrate to the site of infection. Patients undergoing prostatectomies were administered 500 mg of levofloxacin orally every 24 h for 2 days prior to surgery, and then on the day of surgery, 500 mg was administered as an hour-long, constant-rate intravenous (i.v.) infusion. A set of blood samples was obtained as guided by stochastic optimal design theory. Prostate biopsy times were determined by randomizing subjects into one of four groups, based on the interval after the i.v. dose. All plasma and prostate drug concentrations were comodeled by a population modeling program, BigNPEM, implemented on the Cray T3E Supercomputer housed at the Supercomputer Center at the University of California at San Diego. Penetration was determined as the ratio of the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of levofloxacin in the prostate to the plasma levofloxacin AUC. When calculated from the mean population parameters, this penetration ratio was 2.96. We also performed a 1,000-subject Monte Carlo simulation from the mean parameter vector and covariance matrix. The mean penetration ratio here was 4.14 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.20 to 19.6. Over 70% of the population had a penetration ratio in excess of 1.0. Levofloxacin adequately penetrates a noninflamed prostate and should be evaluated for the therapy of prostatitis.
Figures


References
-
- Aagaard J, Madsen P O. Bacterial prostatitis: new methods of treatment. Urology. 1997;37(Suppl.):4–8. - PubMed
-
- Barza M, Cuchural G. General principles of antibiotic tissue penetration. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985;15(Suppl. A):59–75. - PubMed
-
- Cars O. Tissue distribution of ampicillin: assays in muscle tissue and subcutaneous tissue cage fluid from normal and nephrectomized rabbits. Scand J Infect Dis. 1981;13:283–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

