In vitro activity and fecal concentration of rifaximin after oral administration
- PMID: 10898704
- PMCID: PMC90042
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.8.2205-2206.2000
In vitro activity and fecal concentration of rifaximin after oral administration
Abstract
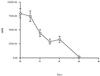
Rifaximin showed moderately high MICs (the MIC at which 90% of the isolates tested were inhibited = 50 microg/ml) for 145 bacterial enteropathogens from patients with traveler's diarrhea acquired in Mexico during the summers of 1997 and 1998. Rifaximin concentrations in stool the day after oral administration (800 mg daily for 3 days) were high (average, 7,961 microg/g), proving the value of the drug.
Figures
References
-
- Corazza G R, Ventrucci M, Strocchi A, Sorge M, Pranzo L, Pezzilli R, Gasbarrini G. Treatment of small intestine bacterial overgrowth with rifaximin, a non-absorbable rifamycin. J Int Med Res. 1988;16:312–316. - PubMed
-
- Descombe J J, Dubourg D, Picard M, Palazzini E. Pharmacokinetic study of rifaximin after oral administration in healthy volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 1994;16:51–56. - PubMed
-
- DuPont H L, Reves R R, Galindo E, Sullivan P S, Wood L V, Mendiola J G. Treatment of travelers' diarrhea with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and with trimethoprim alone. N Engl J Med. 1982;307:841–844. - PubMed
-
- DuPont H L, Ericsson C D. Prevention and treatment of traveler's diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1821–1827. - PubMed
-
- DuPont H L, Ericsson C D, Mathewson J J, Palazzini E, DuPont M W, Jiang Z D, Mosavi A, de la Cabada F J. Rifaximin: a nonabsorbed antimicrobial in the therapy of travelers' diarrhea. Digestion. 1998;59:708–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical