Signaling pathways in insulin action: molecular targets of insulin resistance
- PMID: 10903329
- PMCID: PMC314316
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI10582
Signaling pathways in insulin action: molecular targets of insulin resistance
Figures
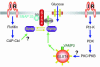
References
-
- Taylor SI, Arioglu E. Syndromes associated with insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 1998;9:419–439. - PubMed
-
- Krook A, O’Rahilly S. Mutant insulin receptors in syndromes of insulin resistance. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;10:97–122. - PubMed
-
- Accili D, et al. Early neonatal death in mice homozygous for a null allele of the insulin receptor gene. Nat Genet. 1996;12:106–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

