Familial primary pulmonary hypertension (gene PPH1) is caused by mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein receptor-II gene
- PMID: 10903931
- PMCID: PMC1287532
- DOI: 10.1086/303059
Familial primary pulmonary hypertension (gene PPH1) is caused by mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein receptor-II gene
Abstract
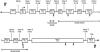
Familial primary pulmonary hypertension is a rare autosomal dominant disorder that has reduced penetrance and that has been mapped to a 3-cM region on chromosome 2q33 (locus PPH1). The phenotype is characterized by monoclonal plexiform lesions of proliferating endothelial cells in pulmonary arterioles. These lesions lead to elevated pulmonary-artery pressures, right-ventricular failure, and death. Although primary pulmonary hypertension is rare, cases secondary to known etiologies are more common and include those associated with the appetite-suppressant drugs, including phentermine-fenfluramine. We genotyped 35 multiplex families with the disorder, using 27 microsatellite markers; we constructed disease haplotypes; and we looked for evidence of haplotype sharing across families, using the program TRANSMIT. Suggestive evidence of sharing was observed with markers GGAA19e07 and D2S307, and three nearby candidate genes were examined by denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography on individuals from 19 families. One of these genes (BMPR2), which encodes bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II, was found to contain five mutations that predict premature termination of the protein product and two missense mutations. These mutations were not observed in 196 control chromosomes. These findings indicate that the bone morphogenetic protein-signaling pathway is defective in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension and may implicate the pathway in the nonfamilial forms of the disease.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- BLAST, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST (for search of HTGS database)
-
- David Clayton's Genetic Programs, http://www.mrc-bsu.cam.ac.uk/pub/methodology/genetics (for TRANSMIT version 2.5 [1999])
-
- Institute of Medical Genetics, University of Wales College of Medicine, Cardiff, http://www.uwcm.ac.uk/uwcm/mg/docs/haha1.html (for disease mutations)
-
- NCBI GenBank Overview, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/GenbankOverview.html (for BMPR2 cDNA sequence number NM_001204)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for PPH [MIM 178600] and HHT [MIM 187300])
References
-
- Abenhaim L, Moride Y, Brenot F, Rich S, Benichou J, Kurz X, Higenbottam T, Oakley C, Wouters E, Aubier M, Simonneau G, Begaud B (1996) Appetite-suppressant drugs and the risk of primary pulmonary hypertension: International Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. N Engl J Med 335:609–616 - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410 - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, Rubin LJ, Long WA, McGoon MD, Rich S, Badesch DB, Groves BM, Tapson VF, Bourge RC, Brundage BH (1996) A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension: The Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. N Engl J Med 334:296–302 - PubMed
-
- Beppu H, Kawabata M, Hamamoto T, Chytil A, Minowa O, Noda T, Miyazono K (2000) BMP type II receptor is required for gastrulation and early development of mouse embryos. Dev Biol 221:249–258 - PubMed
-
- Beppu H, Minowa O, Miyazono K, Kawabata M (1997) cDNA cloning and genomic organization of the mouse BMP type II receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 235:499–504 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

