On the mechanism of ADP-induced alteration of sulphonylurea sensitivity in cardiac ATP-sensitive K(+) channels
- PMID: 10903984
- PMCID: PMC1572183
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703423
On the mechanism of ADP-induced alteration of sulphonylurea sensitivity in cardiac ATP-sensitive K(+) channels
Abstract
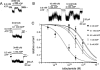
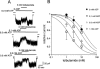
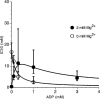
1. To study the mechanism of regulation of sulphonylurea sensitivity in ATP-sensitive K(+) (K(ATP)) channels, we used the inside-out patch clamp technique in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. 2. In the absence of nucleotides, the half maximal concentration of tolbutamide inhibition of K(ATP) channels (IC(50)) was 0.4 mM, and it decreased to 0.1 mM when 0.1 mM ATP was added. 3. Increasing the ADP concentration from 0 to 0.1 and 0.3 mM in the absence of ATP shifted the IC(50) from 0.4 to 5.3 and 11.4 mM, respectively. Increasing the ADP concentration further to 1 and 3 mM conversely reduced the IC(50) to 9.5 and 4.4 mM, respectively. 4. In the absence of Mg(2+) and ADP, the IC(50) was calculated to 16.6 mM which was found to be less, 12.3, 5.1 and 2.5 mM, respectively, when the ADP concentration was increased to 0.1, 0.3 and 1 mM. 5. The IC(50)s for tolbutamide obtained at various concentrations of ADP in the presence of Mg(2+) were best fitted by equations reflecting a model that assumed two binding sites for ADP; one is a high affinity site that reduces the sensitivity to the sulphonylurea, while the other is a low affinity site that increases such sensitivity. Dissociation constants calculated for ADP to sites 1 and 2 were 2.6 microM and 46.7 mM, respectively. In the absence of Mg(2+), data were fitted by equations corresponding to a single site model (site 2); the dissociation constant for ADP was 25.0 mM. 6. It is concluded that ADP modifies tolbutamide sensitivity by binding to two sites. The high affinity site is strongly Mg(2+)-dependent, whereas the low affinity site is Mg(2+)-independent.
Figures
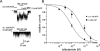
Similar articles
-
Direct activation of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel by oxygen free radicals in guinea-pig ventricular cells: its potentiation by MgADP.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1996 Sep;28(9):1867-77. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1996.0179. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 8899545
-
Sulphonylurea drugs no longer inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ channels during metabolic stress in cardiac muscle.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):456-67. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993. PMID: 8331572
-
Cytosolic nucleotides enhance the tolbutamide sensitivity of the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic B cells by their combined actions at inhibitory and stimulatory receptors.Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):480-6. Mol Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1545776
-
Phosphotransfer reactions in the regulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels.FASEB J. 1998 May;12(7):523-9. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.12.7.523. FASEB J. 1998. PMID: 9576479 Review.
-
Pharmacology and regulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels.Pflugers Arch. 1989;414 Suppl 1:S80-7. doi: 10.1007/BF00582253. Pflugers Arch. 1989. PMID: 2674894 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Development of IKATP Ion Channel Blockers Targeting Sulfonylurea Resistant Mutant KIR6.2 Based Channels for Treating DEND Syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 14;12:814066. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.814066. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35095528 Free PMC article.
-
Mg2+ sensitizes KATP channels to inhibition by DIDS: dependence on the sulphonylurea receptor subunit.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Oct;137(4):429-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704905. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12359624 Free PMC article.
-
Glibenclamide binding to sulphonylurea receptor subtypes: dependence on adenine nucleotides.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Aug;136(7):995-1004. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704801. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12145099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AGUILAR-BRYAN L., NICHOLS C.G., WECHSLER S.W., CLEMENT J.P., IV, BOYD A.E., III, GONZALEZ G., HERRERA-SOSA H., NGUY K., BRYAN J., NELSON D.A. Cloning of the β cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science. 1995;268:423–426. - PubMed
-
- ASHFIELD R., GRIBBLE F.M., ASHCROFT S.J.H., ASHCROFT F.M. Identification of the high-affinity tolbutamide site on the SUR1 subunit of the K(ATP) channel. Diabetes. 1999;48:1341–1347. - PubMed
-
- BAUKROWITZ T., SCHULTE U., OLIVER D., HERLITZE S., KRAUTER T., TUCKER S.J., RUPPERSBERG J.P., FAKLER B. PIP2 and PIP as determinants for ATP inhibition of KATP channels. Science. 1998;282:1141–1144. - PubMed
-
- DÖRSCHNER H., BREKARDIN E., UHDE I., SCHWANSTECHER C., SCHWANSTECHER M. Stoichiometry of sulfonylurea-induced ATP-sensitive potassium channel closure. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999;55:1060–1066. - PubMed
-
- DUNNE M.J., PETERSEN O.H. Intracellular ADP activates K+ channels are that inhibited by ATP in an insulin-secreting cell line. FEBS Lett. 1986;208:59–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

