Modulation of plasma protein binding and in vivo liver cell uptake of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides by cholesterol conjugation
- PMID: 10908328
- PMCID: PMC102653
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.14.2717
Modulation of plasma protein binding and in vivo liver cell uptake of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides by cholesterol conjugation
Abstract
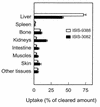
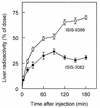
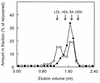
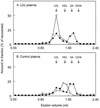
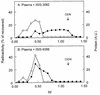
Several studies have shown improved efficacy of cholesteryl-conjugated phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. To gain insight into the mechanisms of the improved efficacy in vivo, we investigated the disposition of ISIS-9388, the 3'-cholesterol analog of the ICAM-1-specific phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotide ISIS-3082, in rats. Intravenously injected [(3)H]ISIS-9388 was cleared from the circulation with a half-life of 49.9 +/- 2.2 min (ISIS-3082, 23.3 +/- 3.8 min). At 3 h after injection, the liver contained 63.7 +/- 3. 3% of the dose. Compared to ISIS-3082, the hepatic uptake of ISIS-9388 is approximately 2-fold higher. Endothelial, Kupffer and parenchymal cells accounted for 45.7 +/- 5.7, 33.0 +/- 5.9 and 21.3 +/- 2.6% of the liver uptake of [(3)H]ISIS-9388, respectively, and intracellular concentrations of approximately 2, 75 and 50 microM, respectively, could be reached in these cells (1 mg/kg dose). Preinjection with polyinosinic acid or poly-adenylic acid reduced the hepatic uptake of [(3)H]ISIS-9388, which suggests the involvement of (multiple) scavenger receptors. Size exclusion chromatography of mixtures of the oligonucleotides and rat plasma indicated that ISIS-9388 binds to a larger extent to high molecular weight proteins than ISIS-3082. Analysis by agarose gel electrophoresis indicated that ISIS-9388 binds more tightly to plasma proteins than ISIS-3082. The different interaction of the oligonucleotides with plasma proteins possibly explains their different dispositions. We conclude that cholesterol conjugation results in high accumulation of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides in various liver cell types, which is likely to be beneficial for antisense therapy of liver-associated diseases.
Figures


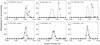
References
-
- Branch A.D. (1996) Hepatology, 24, 1517–1529. - PubMed
-
- Szymkowski D.E. (1996) Drug Discov. Today, 1, 415–428. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar S. and Agrawal,S. (1997) Trends Pharm. Sci., 18, 12–18. - PubMed
-
- Crooke S.T., Graham,M.J., Zuckerman,J.E., Brooks,D., Conklin,B.S., Cummins,L.L., Greig,M.J., Guinosso,C.J., Kornbrust,D., Manoharan,M., Sasmor,H.M., Schleich,T., Tivel,K.L. and Griffey,R.H. (1996) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 277, 923–937. - PubMed
-
- Juliano R.L., Alahari,S., Yoo,H., Kole,R. and Cho,M. (1999) Pharm. Res., 16, 494–502. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

