Regional metabolic patterns in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: A 1H MRS study
- PMID: 10908893
- PMCID: PMC2771162
- DOI: 10.1212/wnl.55.2.210
Regional metabolic patterns in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: A 1H MRS study
Abstract
Background: Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a recently described transitional clinical state between normal aging and AD. Assuming that amnestic MCI patients had pathologic changes corresponding to an early phase and probable AD patients to a later phase of the disease progression, the authors could approximate the temporal course of proton MR spectroscopic (1H MRS) alterations in AD with a cross-sectional sampling scheme.
Methods: The authors compared 1H MRS findings in the superior temporal lobe, posterior cingulate gyri, and medial occipital lobe in 21 patients with MCI, 21 patients with probable AD, and 63 elderly controls. These areas are known to be involved at different neurofibrillary pathologic stages of AD.
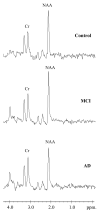
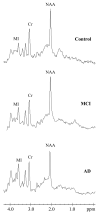
Results: The N-acetylaspartate (NAA)/creatine (Cr) ratios were significantly lower in AD patients compared to both MCI and normal control subjects in the left superior temporal and the posterior cingulate volumes of interest (VOI) and there were no between-group differences in the medial occipital VOI. Myoinositol (MI)/Cr ratios measured from the posterior cingulate VOI were significantly higher in both MCI and AD patients than controls. The choline (Cho)/Cr ratios measured from the posterior cingulate VOI were higher in AD patients compared to both MCI and control subjects.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that the initial 1H MRS change in the pathologic progression of AD is an increase in MI/Cr. A decrease in NAA/Cr and an increase in Cho/Cr develop later in the disease course.
Figures

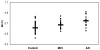
References
-
- Kokmen E, Beard CM, O'Brien PC, Offord K, Kurland LT. Is the incidence of dementing illness changing? A 25- year-time-trend study in Rochester, MN (1960-1984) Neurology. 1993;43:1887–1892. - PubMed
-
- Petersen RC, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ, Kokmen E, Tangalos EG. Memory function in very early Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1994;44:867–872. - PubMed
-
- Minoshima S, Giordani B, Berent S, Frey KA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE. Metabolic reduction in the posterior cingulate cortex in very early Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1997;42:85–94. - PubMed
-
- Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Yun LS, et al. Preclinical evidence of Alzheimer's disease in persons homozygous for the ∈ 4 allele for apolipoprotein E. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:752–758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
