Analysis of the complex relationship between nuclear export and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated gene regulation
- PMID: 10913191
- PMCID: PMC86085
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.16.6095-6104.2000
Analysis of the complex relationship between nuclear export and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated gene regulation
Abstract
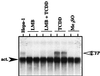
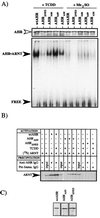
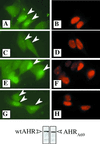
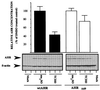
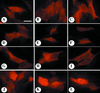
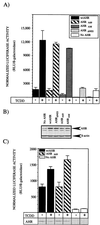
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) contains signals for both nuclear import and nuclear export (NES). The purpose of the studies in this report was to determine the relationship between the nuclear export of the AHR and AHR-mediated gene regulation. Blockage of nuclear export in HepG2 cells with leptomycin B (LMB) resulted in increased levels of AHR-AHR nuclear translocator (ARNT) complex in the nucleus and correlative reductions in agonist-stimulated AHR degradation. However, LMB exposure inhibited agonist-mediated induction of numerous AHR-responsive reporter genes by 75 to 89% and also inhibited induction of endogenous CYP1A1. LMB did not transform the AHR to a ligand binding species or affect activation by TCDD (2, 3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin). Mutagenesis of leucines 66 and 71 of the putative AHR NES resulted in a protein with reduced function in dimerization to ARNT and binding to DNA, while alanine substitution at leucine 69 (AHR(A69)) resulted in an AHR that bound with ARNT and associated with DNA. AHR(A69) protein injected directly into the nuclei of E36 cells remained nuclear following 6 h of agonist stimulation. In transient-transfection assays, AHR(A69) accumulated within the nucleus was not degraded efficiently following agonist exposure. Finally, AHR(A69) supported induction of AHR-responsive reporter genes in an agonist-dependent manner. These findings show that it is possible to generate an AHR protein defective in nuclear export that is functional in agonist-mediated gene induction. This implies that the negative effect of LMB on agonist-mediated gene induction is independent of the nuclear export of the AHR.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.J Biochem. 2000 Mar;127(3):503-9. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022633. J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10731723
-
Regulation of subcellular localization of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR).Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001 May 15;389(2):207-17. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2001.2339. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11339810
-
Functional analysis of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator interactions with aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the yeast two-hybrid system.Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 Oct 12;50(8):1295-302. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)02016-6. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7488247
-
Lack of an absolute requirement for the native aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and AhR nuclear translocator transactivation domains in protein kinase C-mediated modulation of the AhR pathway.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999 Nov 15;371(2):246-59. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1452. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999. PMID: 10545212
-
Induction of CYP1A1. The AhR/DRE paradigm: transcription, receptor regulation, and expanding biological roles.Curr Drug Metab. 2001 Jun;2(2):149-64. doi: 10.2174/1389200013338603. Curr Drug Metab. 2001. PMID: 11469723 Review.
Cited by
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonism and its role in rheumatoid arthritis.J Exp Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 1;7:29-35. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S63549. eCollection 2015. J Exp Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 27186143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcellular Localization Signals of bHLH-PAS Proteins: Their Significance, Current State of Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 24;20(19):4746. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194746. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31554340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carnosol, a constituent of Zyflamend, inhibits aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated activation of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 transcription and mutagenesis.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012 Apr;5(4):593-602. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0002. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012. Retraction in: Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2022 Jun 2;15(6):412. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-22-0203. PMID: 22374940 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A novel heterodimerization domain, CRM1, and 14-3-3 control subcellular localization of the MondoA-Mlx heterocomplex.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;22(24):8514-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.24.8514-8526.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12446771 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in mesenchymal stromal cells: new frontiers in AhR biology.FEBS J. 2021 Jul;288(13):3962-3972. doi: 10.1111/febs.15599. Epub 2020 Nov 1. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33064873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basci S G, Hankinson O. Functional characterization of DNA binding domains of the heterodimeric AHR complex imputing canonical bHLH protein-DNA interactions. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:8843–8850. - PubMed
-
- Carvan M J, Ponomareva L V, Solis W A, Matlib R S, Puga A, Nebert D W. Trout CYP1A3 gene: recognition of fish DNA motifs by mouse regulatory proteins. Mar Biotechnol. 1999;1:155–166. - PubMed
-
- Davarinos N A, Pollenz R S. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor imported into the nucleus following ligand binding is rapidly degraded via the cytoplasmic proteasome following nuclear export. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:28707–28715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
