Comparative characterization of complete and truncated forms of Lactobacillus amylovorus alpha-amylase and role of the C-terminal direct repeats in raw-starch binding
- PMID: 10919790
- PMCID: PMC92154
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.8.3350-3356.2000
Comparative characterization of complete and truncated forms of Lactobacillus amylovorus alpha-amylase and role of the C-terminal direct repeats in raw-starch binding
Abstract
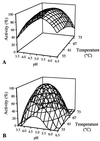
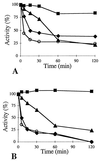
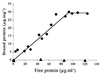
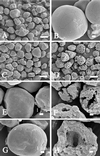
Two constructs derived from the alpha-amylase gene (amyA) of Lactobacillus amylovorus were expressed in Lactobacillus plantarum, and their expression products were purified, characterized, and compared. These products correspond to the complete (AmyA) and truncated (AmyADelta) forms of alpha-amylase; AmyADelta lacks the 66-kDa carboxyl-terminal direct-repeating-unit region. AmyA and AmyADelta exhibit similar amylase activities towards a range of soluble substrates (amylose, amylopectin and alpha-cyclodextrin, and soluble starch). The specific activities of the enzymes towards soluble starch are similar, but the K(M) and V(max) values of AmyADelta were slightly higher than those of AmyA, whereas the thermal stability of AmyADelta was lower than that of AmyA. In contrast to AmyA, AmyADelta is unable to bind to beta-cyclodextrin and is only weakly active towards glycogen. More striking is the fact that AmyADelta cannot bind or hydrolyze raw starch, demonstrating that the carboxyl-terminal repeating-unit domain of AmyA is required for raw-starch binding activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Starch-binding domain affects catalysis in two Lactobacillus alpha-amylases.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jan;71(1):297-302. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.1.297-302.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15640201 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and comparative characterization of complete and C-terminally truncated forms of saccharifying α-amylase from Lactobacillus plantarum S21.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Oct;103:1294-1301. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.168. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28587961
-
Molecular characterization of the alpha-amylase genes of Lactobacillus plantarum A6 and Lactobacillus amylovorus reveals an unusual 3' end structure with direct tandem repeats and suggests a common evolutionary origin.Gene. 1997 Oct 1;198(1-2):149-57. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00309-0. Gene. 1997. PMID: 9370276
-
Isolation, characterization and inhibition by acarbose of the alpha-amylase from Lactobacillus fermentum: comparison with Lb. manihotivorans and Lb. plantarum amylases.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2002 Nov;133(3):351-60. doi: 10.1016/s1096-4959(02)00157-4. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12431403
-
New type of starch-binding domain: the direct repeat motif in the C-terminal region of Bacillus sp. no. 195 alpha-amylase contributes to starch binding and raw starch degrading.Biochem J. 2000 Sep 1;350 Pt 2(Pt 2):477-84. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10947962 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Starch-binding domain affects catalysis in two Lactobacillus alpha-amylases.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jan;71(1):297-302. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.1.297-302.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15640201 Free PMC article.
-
AmyJ33, a truncated amylase with improved catalytic properties.Biotechnol Lett. 2022 Dec;44(12):1447-1463. doi: 10.1007/s10529-022-03311-5. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Biotechnol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36326957
-
α-Amylase: an enzyme specificity found in various families of glycoside hydrolases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Apr;71(7):1149-70. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1388-z. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 23807207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving the thermostability of raw-starch-digesting amylase from a Cytophaga sp. by site-directed mutagenesis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Apr;69(4):2383-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.4.2383-2385.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12676725 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-amylase starch binding domains: cooperative effects of binding to starch granules of multiple tandemly arranged domains.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Jun;73(12):3833-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02628-06. Epub 2007 Apr 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17468268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blakesly R W, Boezi J A. A new staining technique for protein in polyacrylamide gels using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250. Anal Biochem. 1977;82:580–582. - PubMed
-
- Bohak I, Back W, Richter L, Eirman M, Ludwig W, Schleifer K H. Lactobacillus amylolyticus sp. nov., isolated from beer malt and beer wort. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1998;21:360–364. - PubMed
-
- Box G E P, Hunter W G, Hunter J S. Statistics for experimenters: an introduction to design, data analysis, and model building. New York, N.Y: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.; 1978.
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Coutinho P M, Nikolov Z, Ford C. Deletions analysis of the starch-binding domain of Aspergillus glucoamylase. Protein Eng. 1995;8:1049–1055. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

