Anaerobic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae carrying XYL1, XYL2, and XKS1 in mineral medium chemostat cultures
- PMID: 10919795
- PMCID: PMC92159
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.8.3381-3386.2000
Anaerobic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae carrying XYL1, XYL2, and XKS1 in mineral medium chemostat cultures
Abstract
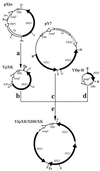
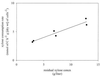
For ethanol production from lignocellulose, the fermentation of xylose is an economic necessity. Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been metabolically engineered with a xylose-utilizing pathway. However, the high ethanol yield and productivity seen with glucose have not yet been achieved. To quantitatively analyze metabolic fluxes in recombinant S. cerevisiae during metabolism of xylose-glucose mixtures, we constructed a stable xylose-utilizing recombinant strain, TMB 3001. The XYL1 and XYL2 genes from Pichia stipitis, encoding xylose reductase (XR) and xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH), respectively, and the endogenous XKS1 gene, encoding xylulokinase (XK), under control of the PGK1 promoter were integrated into the chromosomal HIS3 locus of S. cerevisiae CEN.PK 113-7A. The strain expressed XR, XDH, and XK activities of 0.4 to 0.5, 2.7 to 3.4, and 1.5 to 1.7 U/mg, respectively, and was stable for more than 40 generations in continuous fermentations. Anaerobic ethanol formation from xylose by recombinant S. cerevisiae was demonstrated for the first time. However, the strain grew on xylose only in the presence of oxygen. Ethanol yields of 0.45 to 0.50 mmol of C/mmol of C (0.35 to 0.38 g/g) and productivities of 9.7 to 13.2 mmol of C h(-1) g (dry weight) of cells(-1) (0.24 to 0.30 g h(-1) g [dry weight] of cells(-1)) were obtained from xylose-glucose mixtures in anaerobic chemostat cultures, with a dilution rate of 0.06 h(-1). The anaerobic ethanol yield on xylose was estimated at 0.27 mol of C/(mol of C of xylose) (0.21 g/g), assuming a constant ethanol yield on glucose. The xylose uptake rate increased with increasing xylose concentration in the feed, from 3.3 mmol of C h(-1) g (dry weight) of cells(-1) when the xylose-to-glucose ratio in the feed was 1:3 to 6.8 mmol of C h(-1) g (dry weight) of cells(-1) when the feed ratio was 3:1. With a feed content of 15 g of xylose/liter and 5 g of glucose/liter, the xylose flux was 2.2 times lower than the glucose flux, indicating that transport limits the xylose flux.
Figures
References
-
- Andreasen A A, Stier T J B. Anaerobic nutrition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Ergosterol requirement for growth in a defined medium. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1953;41:23–36. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen A A, Stier T J B. Anaerobic nutrition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Unsaturated fatty acid requirement for growth in a defined medium. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1954;43:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Berben G, Dumont J, Gilliquet V, Bolle P-A, Hilger F. The YDp plasmids: a uniform set of vectors bearing versatile gene disruption cassettes for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1991;7:475–477. - PubMed
-
- Bergmeyer H U, editor. Methods of enzymatic analysis. 2nd ed. Vol. 1. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1974.
-
- Boles E, Heinisch J, Zimmermann F K. Different signals control the activation of glycolysis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1993;9:761–770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

