COP I domains required for coatomer integrity, and novel interactions with ARF and ARF-GAP
- PMID: 10921873
- PMCID: PMC306616
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.3905
COP I domains required for coatomer integrity, and novel interactions with ARF and ARF-GAP
Abstract
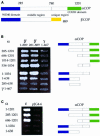
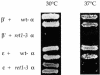
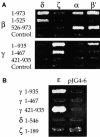
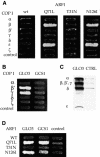
We performed a systematic mapping of interaction domains on COP I subunits to gain novel insights into the architecture of coatomer. Using the two-hybrid system, we characterize the domain structure of the alpha-, beta'-, epsilon-COP and beta-, gamma-, delta-, zeta-COP coatomer subcomplexes and identify links between them that contribute to coatomer integrity. Our results demonstrate that the domain organization of the beta-, gamma-, delta-, zeta-COP subcomplex and AP adaptor complexes is related. Through in vivo analysis of alpha-COP truncation mutants, we characterize distinct functional domains on alpha-COP. Its N-terminal WD40 domain is dispensable for yeast cell viability and overall coatomer function, but is required for KKXX-dependent trafficking. The last approximately 170 amino acids of alpha-COP are also non-essential for cell viability, but required for epsilon-COP incorporation into coatomer and maintainance of normal epsilon-COP levels. Further, we demonstrate novel direct interactions of coatomer subunits with regulatory proteins: beta'- and gamma-COP interact with the ARF-GTP-activating protein (GAP) Glo3p, but not Gcs1p, and beta- and epsilon-COP interact with ARF-GTP. Glo3p also interacts with intact coatomer in vitro.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multiple and stepwise interactions between coatomer and ADP-ribosylation factor-1 (Arf1)-GTP.Traffic. 2007 May;8(5):582-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00554.x. Traffic. 2007. PMID: 17451557
-
Solution structure of human zeta-COP: direct evidences for structural similarity between COP I and clathrin-adaptor coats.J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 6;386(4):903-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.12.083. Epub 2009 Jan 10. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19167404
-
The alpha- and beta'-COP WD40 domains mediate cargo-selective interactions with distinct di-lysine motifs.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Mar;15(3):1011-23. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-10-0724. Epub 2003 Dec 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 14699056 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome biogenesis: where Arf and coatomer might be involved.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Dec;1763(12):1678-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.08.036. Epub 2006 Aug 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 17023067 Review.
-
Arf GAPs and membrane traffic.J Cell Sci. 2006 Apr 1;119(Pt 7):1203-11. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02924. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16554436 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic structure-function analysis of the small GTPase Arf1 in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 May;13(5):1652-64. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-01-0007. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12006660 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of COPA syndrome.Appl Clin Genet. 2019 Feb 8;12:11-18. doi: 10.2147/TACG.S153600. eCollection 2019. Appl Clin Genet. 2019. PMID: 30804679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TBC1D5-Catalyzed Cycling of Rab7 Is Required for Retromer-Mediated Human Papillomavirus Trafficking during Virus Entry.Cell Rep. 2020 Jun 9;31(10):107750. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107750. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32521275 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced secretion of a methyl parathion hydrolase in Pichia pastoris using a combinational strategy.Microb Cell Fact. 2015 Aug 28;14:123. doi: 10.1186/s12934-015-0315-4. Microb Cell Fact. 2015. PMID: 26310666 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated Plasma Membrane Turnover Underlying Dendritic Pathology in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Oct 6;14:556461. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.556461. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33192307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conibear E. and Stevens,T.H. (1998) Multiple sorting pathways between the late Golgi and the vacuole in yeast. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1404, 211–230. - PubMed
-
- Cosson P. and Letourneur,F. (1994) Coatomer interaction with di-lysine endoplasmic reticulum retention motifs. Science, 263, 1629–1631. - PubMed
-
- Dascher C. and Balch,W.E. (1994) Dominant inhibitory mutants of ARF1 block endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport and trigger disassembly of the Golgi apparatus. J. Biol. Chem., 269, 1437–1448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

