Targeting of N-CoR and histone deacetylase 3 by the oncoprotein v-erbA yields a chromatin infrastructure-dependent transcriptional repression pathway
- PMID: 10921888
- PMCID: PMC306612
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.4074
Targeting of N-CoR and histone deacetylase 3 by the oncoprotein v-erbA yields a chromatin infrastructure-dependent transcriptional repression pathway
Abstract
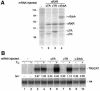
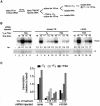
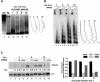
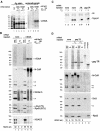
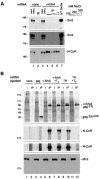
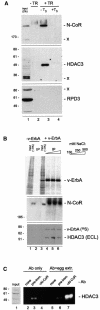
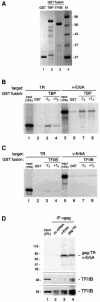
Transcriptional repression by nuclear hormone receptors is thought to result from a unison of targeting chromatin modification and disabling the basal transcriptional machinery. We used Xenopus oocytes to compare silencing effected by the thyroid hormone receptor (TR) and its mutated version, the oncoprotein v-ErbA, on partly and fully chromatinized TR-responsive templates in vivo. Repression by v-ErbA was not as efficient as that mediated by TR, was significantly more sensitive to histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor treatment and, unlike TR, v-ErbA required mature chromatin to effect repression. We find that both v-ErbA and TR can recruit the corepressor N-CoR, but, in contrast to existing models, show a concomitant enrichment for HDAC3 that occurs without an association with Sin3, HDAC1/RPD3, Mi-2 or HDAC5. We propose a requirement for chromatin infrastructure in N-CoR/HDAC3-effected repression and suggest that the inability of v-ErbA to silence on partly chromatinized templates may stem from its impaired capacity to interfere with basal transcriptional machinery function. In support of this notion, we find v-ErbA to be less competent than TR for binding to TFIIB in vitro and in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specific targeting and constitutive association of histone deacetylase complexes during transcriptional repression.Genes Dev. 2002 Mar 15;16(6):687-92. doi: 10.1101/gad.962502. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 11914274 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemic transformation by the v-ErbA oncoprotein entails constitutive binding to and repression of an erythroid enhancer in vivo.EMBO J. 1998 Dec 15;17(24):7382-94. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.24.7382. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9857194 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct requirements for chromatin assembly in transcriptional repression by thyroid hormone receptor and histone deacetylase.EMBO J. 1998 Jan 15;17(2):520-34. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.2.520. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9430643 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of thyroid hormone receptor silencing function by co-repressors and a synergizing transcription factor.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):386-9. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961925 Review.
-
Co-repressor complexes and remodelling chromatin for repression.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):379-86. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10961924 Review.
Cited by
-
JDP2, a repressor of AP-1, recruits a histone deacetylase 3 complex to inhibit the retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(13):4815-26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.13.4815-4826.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12052888 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin disruption and histone acetylation in regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat by thyroid hormone receptor.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;22(12):4043-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4043-4052.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12024018 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce remission in transgenic models of therapy-resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia.J Clin Invest. 2001 Nov;108(9):1321-30. doi: 10.1172/JCI11537. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11696577 Free PMC article.
-
The N-CoR/histone deacetylase 3 complex is required for repression by thyroid hormone receptor.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;23(15):5122-31. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.15.5122-5131.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12861000 Free PMC article.
-
The highly conserved region of the co-repressor Sin3A functionally interacts with the co-repressor Alien.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jun 1;32(10):2995-3004. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh621. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15173382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams C.R. and Kamakaka,R.T. (1999) Chromatin assembly: biochemical identities and genetic redundancy. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 9, 185–190. - PubMed
-
- Almouzni G. and Wolffe,A.P. (1993a) Nuclear assembly, structure, and function: the use of Xenopus in vitro systems. Exp. Cell Res., 205, 1–15. - PubMed
-
- Almouzni G. and Wolffe,A.P. (1993b) Replication-coupled chromatin assembly is required for the repression of basal transcription in vivo. Genes Dev., 7, 2033–2047. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

