Selective stimulation of translation of leaderless mRNA by initiation factor 2: evolutionary implications for translation
- PMID: 10921890
- PMCID: PMC306601
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.15.4101
Selective stimulation of translation of leaderless mRNA by initiation factor 2: evolutionary implications for translation
Abstract
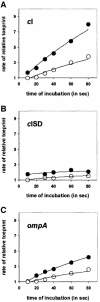
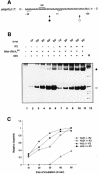
Translation initiation in bacteria involves a stochastic binding mechanism in which the 30S ribosomal subunit first binds either to mRNA or to initiator tRNA, fMet-tRNA(f)(Met). Leaderless lambda cI mRNA did not form a binary complex with 30S ribosomes, which argues against the view that ribosomal recruitment signals other than a 5'-terminal start codon are essential for translation initiation of these mRNAs. We show that, in Escherichia coli, translation initiation factor 2 (IF2) selectively stimulates translation of lambda cI mRNA in vivo and in vitro. These experiments suggest that the start codon of leaderless mRNAs is recognized by a 30S-fMet-tRNA(f)(Met)-IF2 complex, an intermediate equivalent to that obligatorily formed during translation initiation in eukaryotes. We further show that leaderless lambda cI mRNA is faithfully translated in vitro in both archaebacterial and eukaryotic translation systems. This suggests that translation of leaderless mRNAs reflects a fundamental capability of the translational apparatus of all three domains of life and lends support to the hypothesis that the translation initiation pathway is universally conserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A leaderless mRNA can bind to mammalian 80S ribosomes and direct polypeptide synthesis in the absence of translation initiation factors.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):3164-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.3164-3169.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581790 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the 30S translation initiation complex.Nature. 2008 Sep 18;455(7211):416-20. doi: 10.1038/nature07192. Epub 2008 Aug 31. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18758445
-
Modulation of ribosomal recruitment to 5'-terminal start codons by translation initiation factors IF2 and IF3.FEBS Lett. 2001 Apr 27;495(3):167-71. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02378-x. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11334885
-
Leaderless mRNAs in bacteria: surprises in ribosomal recruitment and translational control.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Jan;43(1):239-46. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02739.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11849551 Review.
-
Evolution and the universality of the mechanism of initiation of protein synthesis.Gene. 2009 Mar 1;432(1-2):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.11.001. Epub 2008 Nov 8. Gene. 2009. PMID: 19056476 Review.
Cited by
-
Genes of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis from the hyperthermoacidophilic crenarchaeote Sulfolobus acidocaldarius: novel organization in a bipolar operon.J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug;184(16):4430-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.16.4430-4441.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12142413 Free PMC article.
-
Four translation initiation pathways employed by the leaderless mRNA in eukaryotes.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 28;6:37905. doi: 10.1038/srep37905. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27892500 Free PMC article.
-
Extreme secretion: protein translocation across the archael plasma membrane.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004 Feb;36(1):35-45. doi: 10.1023/b:jobb.0000019596.76554.7a. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004. PMID: 15168608 Review.
-
The Impact of Leadered and Leaderless Gene Structures on Translation Efficiency, Transcript Stability, and Predicted Transcription Rates in Mycobacterium smegmatis.J Bacteriol. 2020 Apr 9;202(9):e00746-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00746-19. Print 2020 Apr 9. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32094162 Free PMC article.
-
Why is start codon selection so precise in eukaryotes?Translation (Austin). 2014 Mar 12;2(1):e28387. doi: 10.4161/trla.28387. eCollection 2014. Translation (Austin). 2014. PMID: 26779403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bläsi U., Kalousek,S. and Lubitz,W. (1990) A bifunctional vector system for controlled expression and subsequent release of the cloned gene product by ΦX174 lysis protein-E. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 33, 564–568. - PubMed
-
- Bläsi U., O’Connor,M., Squires,C.L. and Dahlberg,A.E. (1999) Misled by sequence complementarity: does the DB–anti-DB interaction withstand scientific scrutiny? Mol. Microbiol., 33, 439–441. - PubMed
-
- Boni I.V., Zlatkin,I.V. and Budowsky,E.I. (1982) Ribosomal protein S1 associates with the Escherichia coli ribosomal 30S subunit by means of protein–protein interactions. Eur. J. Biochem., 121, 371–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

