p300-mediated acetylation facilitates the transfer of histone H2A-H2B dimers from nucleosomes to a histone chaperone
- PMID: 10921904
- PMCID: PMC316828
p300-mediated acetylation facilitates the transfer of histone H2A-H2B dimers from nucleosomes to a histone chaperone
Abstract
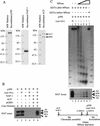
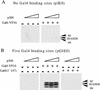
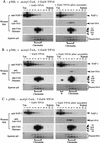
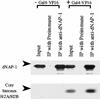
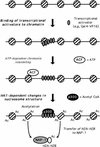
We have used a purified recombinant chromatin assembly system, including ACF (Acf-1 + ISWI) and NAP-1, to examine the role of histone acetylation in ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling. The binding of a transcriptional activator (Gal4-VP16) to chromatin assembled using this recombinant assembly system dramatically enhances the acetylation of nucleosomal core histones by the histone acetyltransferase p300. This effect requires both the presence of Gal4-binding sites in the template and the VP16-activation domain. Order-of-addition experiments indicate that prior activator-meditated, ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling by ACF is required for the acetylation of nucleosomal histones by p300. Thus, chromatin remodeling, which requires a transcriptional activator, ACF and ATP, is an early step in the transcriptional process that regulates subsequent core histone acetylation. Glycerol gradient sedimentation and immunoprecipitation assays demonstrate that the acetylation of histones by p300 facilitates the transfer of H2A-H2B from nucleosomes to NAP-1. The results from these biochemical experiments suggest that (1) transcriptional activators (e.g., Gal4-VP16) and chromatin remodeling complexes (e.g., ACF) induce chromatin remodeling in the absence of histone acetylation; (2) transcriptional activators recruit histone acetyltransferases (e.g., p300) to promoters after chromatin remodeling has occurred; and (3) histone acetylation is important for a step subsequent to chromatin remodeling and results in the transfer of histone H2A-H2B dimers from nucleosomes to a histone chaperone such as NAP-1. Our results indicate a precise role for histone acetylation, namely to alter the structure of nucleosomes (e.g., facilitate the loss of H2A-H2B dimers) that have been remodeled previously by the action of ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes. Thus, transcription from chromatin templates is ordered and sequential, with precise timing and roles for ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling, subsequent histone acetylation, and alterations in nucleosome structure.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SWI/SNF remodeling and p300-dependent transcription of histone variant H2ABbd nucleosomal arrays.EMBO J. 2004 Oct 1;23(19):3815-24. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600400. Epub 2004 Sep 16. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15372075 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of polymerase II transcription repression by the histone variant macroH2A.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;26(3):1156-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.3.1156-1164.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16428466 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly and disassembly of nucleosome core particles containing histone variants by human nucleosome assembly protein I.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(23):10639-51. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10639-10651.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16287874 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling chromatin structures for transcription: what happens to the histones?Bioessays. 1996 Nov;18(11):875-84. doi: 10.1002/bies.950181106. Bioessays. 1996. PMID: 8939065 Review.
-
Chromatin remodeling complexes: ATP-dependent machines in action.Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;83(4):405-17. doi: 10.1139/o05-115. Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16094444 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylation of retinal histones in diabetes increases inflammatory proteins: effects of minocycline and manipulation of histone acetyltransferase (HAT) and histone deacetylase (HDAC).J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 27;287(31):25869-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.375204. Epub 2012 May 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22648458 Free PMC article.
-
The histone chaperone TAF-I/SET/INHAT is required for transcription in vitro of chromatin templates.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;25(2):797-807. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.2.797-807.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15632079 Free PMC article.
-
Dual roles of p300 in chromatin assembly and transcriptional activation in cooperation with nucleosome assembly protein 1 in vitro.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(9):2974-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.9.2974-2983.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11940655 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA DIGIT and BRD3 protein form phase-separated condensates to regulate endoderm differentiation.Nat Cell Biol. 2020 Oct;22(10):1211-1222. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0572-2. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Nat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32895492 Free PMC article.
-
Compaction kinetics on single DNAs: purified nucleosome reconstitution systems versus crude extract.Biophys J. 2005 Nov;89(5):3647-59. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.062786. Epub 2005 Aug 12. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 16100259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature. 1996;384:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Cosma MP, Tanaka T, Nasmyth K. Ordered recruitment of transcription and chromatin remodeling factors to a cell cycle- and developmentally regulated promoter. Cell. 1999;97:299–311. - PubMed
-
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin unfolds. Cell. 1996;86:13–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
