members only encodes a Drosophila nucleoporin required for rel protein import and immune response activation
- PMID: 10921908
- PMCID: PMC316830
members only encodes a Drosophila nucleoporin required for rel protein import and immune response activation
Abstract
Many developmental and physiological responses rely on the selective translocation of transcriptional regulators in and out of the nucleus through the nuclear pores. Here we describe the Drosophila gene members only (mbo) encoding a nucleoporin homologous to the mammalian Nup88. The phenotypes of mbo mutants and mbo expression during development are cell specific, indicating that the nuclear import capacity of cells is differentially regulated. Using inducible assays for nucleocytoplasmic trafficking we show that mRNA export and classic NLS-mediated protein import are unaffected in mbo mutants. Instead, mbo is selectively required for the nuclear import of the yeast transcription factor GAL4 in a subset of the larval tissues. We have identified the first endogenous targets of the mbo nuclear import pathway in the Rel proteins Dorsal and Dif. In mbo mutants the upstream signaling events leading to the degradation of the IkappaB homolog Cactus are functional, but Dorsal and Dif remain cytoplasmic and the larval immune response is not activated in response to infection. Our results demonstrate that distinct nuclear import events require different nucleoporins in vivo and suggest a regulatory role for mbo in signal transduction.
Figures

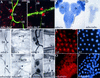
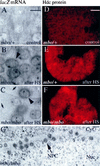
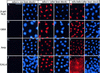
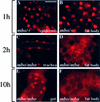

References
-
- Aspland SE, White RA. Nucleocytoplasmic localisation of extradenticle protein is spatially regulated throughout development in Drosophila. Development. 1997;124:741–747. - PubMed
-
- Bray SJ, Kafatos FC. Developmental function of Elf-1: An essential transcription factor during embryogenesis in Drosophila. Genes & Dev. 1991;5:1672–1683. - PubMed
-
- Briggs LJ, Stein D, Goltz J, Corrigan VC, Efthymiadis A, Hübner S, Jans DA. The cAMP-dependent protein kinase site (Ser312) enhances dorsal nuclear import through facilitating nuclear localization sequence/importin interaction. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:22745–22752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
