Performance characteristics of the QUANTIPLEX HIV-1 RNA 3.0 assay for detection and quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma
- PMID: 10921936
- PMCID: PMC87124
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.8.2837-2845.2000
Performance characteristics of the QUANTIPLEX HIV-1 RNA 3.0 assay for detection and quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma
Abstract
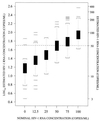
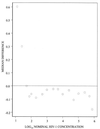
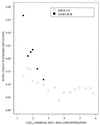
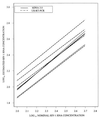
The QUANTIPLEX HIV-1 RNA assay, version 3.0 (a branched DNA, version 3.0, assay [bDNA 3.0 assay]), was evaluated by analyzing spiked and clinical plasma samples and was compared with the AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR Ultrasensitive (ultrasensitive reverse transcription-PCR [US-RT-PCR]) method. A panel of spiked plasma samples that contained 0 to 750,000 copies of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA per ml was tested four times in each of four laboratories (1,344 assays). Negative results (<50 copies/ml) were obtained in 30 of 32 (94%) assays with seronegative samples, 66 of 128 (52%) assays with HIV-1 RNA at 50 copies/ml, and 5 of 128 (4%) assays with HIV-1 RNA at 100 copies/ml. The assay was linear from 100 to 500,000 copies/ml. The within-run standard deviation (SD) of the log(10) estimated HIV-1 RNA concentration was 0.08 at 1,000 to 500,000 copies/ml, increased below 1,000 copies/ml, and was 0.17 at 100 copies/ml. Between-run reproducibility at 100 to 500 copies/ml was <0.10 log(10) in most comparisons. Interlaboratory differences across runs were </=0.10 log(10) at all concentrations examined. A subset of the panel (25 to 500 copies/ml) was also analyzed by the US-RT-PCR assay. The within-run SD varied inversely with the log(10) HIV-1 RNA concentration but was higher than the SD for the bDNA 3.0 assay at all concentrations. Log-log regression analysis indicated that the two methods produced very similar estimates at 100 to 500 copies/ml. In parallel testing of clinical specimens with low HIV-1 RNA levels, 80 plasma samples with <50 copies/ml by the US-RT-PCR assay had <50 copies/ml when they were retested by the bDNA 3.0 assay. In contrast, 11 of 78 (14%) plasma samples with <50 copies/ml by the bDNA 3.0 assay had >/=50 copies/ml when they were retested by the US-RT-PCR assay (median, 86 copies/ml; range, 50 to 217 copies/ml). Estimation of bDNA 3.0 values of <50 copies/ml by extending the standard curve of the assay showed that these samples with discrepant results had higher HIV-1 RNA levels than the samples with concordant results (median, 34 versus 17 copies/ml; P = 0.0051 by the Wilcoxon two-sample test). The excellent reproducibility, broad linear range, and good sensitivity of the bDNA 3.0 assay make it a very attractive method for quantitation of HIV-1 RNA levels in plasma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical comparison of an enhanced-sensitivity branched-DNA assay and reverse transcription-PCR for quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma.J Clin Microbiol. 1998 Mar;36(3):716-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.36.3.716-720.1998. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9508301 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter comparison of Roche COBAS AMPLICOR MONITOR version 1.5, Organon Teknika NucliSens QT with Extractor, and Bayer Quantiplex version 3.0 for quantification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Nov;38(11):4034-41. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.11.4034-4041.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11060065 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of the QUANTIPLEX HIV-1 RNA 2.0 and 3.0 (bDNA) assays and the AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR v1.5 test for the quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA in plasma.J Virol Methods. 2001 Jan;91(1):67-74. doi: 10.1016/s0166-0934(00)00245-7. J Virol Methods. 2001. PMID: 11164487
-
Quantitative and cost comparison of ultrasensitive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA viral load assays: Bayer bDNA quantiplex versions 3.0 and 2.0 and Roche PCR Amplicor monitor version 1.5.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Mar;38(3):1113-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.3.1113-1120.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10699005 Free PMC article.
-
New tools for quantifying HIV-1 reservoirs: plasma RNA single copy assays and beyond.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2012 Mar;9(1):91-100. doi: 10.1007/s11904-011-0104-6. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2012. PMID: 22215419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RT-PCR detection of HIV in Republic of Macedonia.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2008 Nov;8(4):350-5. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2008.2896. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2008. PMID: 19125707 Free PMC article.
-
HIV dynamics in seminal plasma during primary HIV infection.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2008 Oct;24(10):1269-74. doi: 10.1089/aid.2008.0014. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2008. PMID: 18844461 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time PCR quantification of genital shedding of herpes simplex virus (HSV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in women coinfected with HSV and HIV.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Feb;44(2):423-32. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.2.423-432.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16455895 Free PMC article.
-
Highly sensitive multiplex assay for detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and hepatitis C virus RNA.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Jul;40(7):2408-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.7.2408-2419.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12089255 Free PMC article.
-
Intra- and interlaboratory variabilities of results obtained with the Quantiplex human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA bDNA assay, version 3.0.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001 May;8(3):560-3. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.8.3.560-563.2001. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11329458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown A E, Jackson B, Fuller S A, Sheffield J, Cannon M A, Lane J R. Viral RNA in the resolution of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 diagnostic serology. Transfusion. 1997;37:926–929. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter C C J, Cooper D A, Fischl M A, Gatell J M, Gazzard B G, Hammer S M, Hirsch M S, Jacobsen D M, Katzenstein D A, Montaner J S G, Richman D D, Saag M S, Schechter M, Schooley R T, Thompson M A, Vella S, Yeni P G, Volberding P A. Antiretroviral therapy in adults. Updated recommendations of the International AIDS Society-USA panel. JAMA. 2000;283:381–390. - PubMed
-
- Dornadula G, Zhang H, VanUitert B, Stern J, Livornese L, Ingerman M J, Witek J, Kedanis R J, Natkin J, DeSimone J, Pomerantz R J. Residual HIV-1 RNA in blood plasma of patients taking suppressive highly active antiretroviral therapy. JAMA. 1999;282:1627–1632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

