Evaluation of recA sequences for identification of Mycobacterium species
- PMID: 10921937
- PMCID: PMC87126
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.8.2846-2852.2000
Evaluation of recA sequences for identification of Mycobacterium species
Abstract
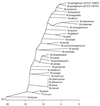
16S rRNA sequence data have been used to provide a molecular basis for an accurate system for identification of members of the genus Mycobacterium. Previous studies have shown that Mycobacterium species demonstrate high levels (>94%) of 16S rRNA sequence similarity and that this method cannot differentiate between all species, i.e., M. gastri and M. kansasii. In the present study, we have used the recA gene as an alternative sequencing target in order to complement 16S rRNA sequence-based genetic identification. The recA genes of 30 Mycobacterium species were amplified by PCR, sequenced, and compared with the published recA sequences of M. tuberculosis, M. smegmatis, and M. leprae available from GenBank. By recA sequencing the species showed a lower degree of interspecies similarity than they did by 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, ranging from 96.2% between M. gastri and M. kansasii to 75.7% between M. aurum and M. leprae. Exceptions to this were members of the M. tuberculosis complex, which were identical. Two strains of each of 27 species were tested, and the intraspecies similarity ranged from 98.7 to 100%. In addition, we identified new Mycobacterium species that contain a protein intron in their recA genes, similar to M. tuberculosis and M. leprae. We propose that recA gene sequencing offers a complementary method to 16S rRNA gene sequencing for the accurate identification of the Mycobacterium species.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dissection of phylogenetic relationships among 19 rapidly growing Mycobacterium species by 16S rRNA, hsp65, sodA, recA and rpoB gene sequencing.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2004 Nov;54(Pt 6):2095-2105. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63094-0. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15545441
-
Application of recA and rpoB sequence analysis on phylogeny and molecular identification of Geobacillus species.J Appl Microbiol. 2009 Aug;107(2):452-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04235.x. Epub 2009 Apr 23. J Appl Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19426278
-
Identification of Bacillus Probiotics Isolated from Soil Rhizosphere Using 16S rRNA, recA, rpoB Gene Sequencing and RAPD-PCR.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2016 Mar;8(1):8-18. doi: 10.1007/s12602-016-9208-z. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2016. PMID: 26898909
-
Identification of Mycobacterium neoaurum isolated from a neutropenic patient with catheter-related bacteremia by 16S rRNA sequencing.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Sep;38(9):3515-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.9.3515-3517.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10970421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Mycobacterium shinshuense and Mycobacterium leprae infections: usefulness of genetical examinations].Nihon Hansenbyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2007 Sep;76(3):245-50. doi: 10.5025/hansen.76.245. Nihon Hansenbyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17877036 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Phylogenetic framework and molecular signatures for the main clades of the phylum Actinobacteria.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Mar;76(1):66-112. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05011-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22390973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Necessity of quality-controlled 16S rRNA gene sequence databases: identifying nontuberculous Mycobacterium species.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Oct;39(10):3637-48. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.10.3638-3648.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11574585 Free PMC article.
-
Description of Mycobacterium conceptionense sp. nov., a Mycobacterium fortuitum group organism isolated from a posttraumatic osteitis inflammation.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Apr;44(4):1268-73. doi: 10.1128/JCM.44.4.1268-1273.2006. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16597850 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial classification of fish-pathogenic Mycobacterium species by multigene phylogenetic analyses and MALDI Biotyper identification system.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2013 Jun;15(3):340-8. doi: 10.1007/s10126-012-9492-x. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2013. PMID: 23229498
-
Use of PCR and reverse line blot hybridization macroarray based on 16S-23S rRNA gene internal transcribed spacer sequences for rapid identification of 34 mycobacterium species.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Oct;44(10):3544-50. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00633-06. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17021080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clayton R A, Sutton G, Hinkle P S, Bult C, Fields C. Intraspecific variation in small-subunit rRNA sequences in GenBank: why single sequences may not adequately represent prokaryotic taxa. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1995;45:595–599. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

