Nosocomial transmission of echovirus 30: molecular evidence by phylogenetic analysis of the VP1 encoding sequence
- PMID: 10921945
- PMCID: PMC87138
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.8.2889-2892.2000
Nosocomial transmission of echovirus 30: molecular evidence by phylogenetic analysis of the VP1 encoding sequence
Abstract
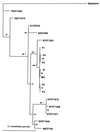
We investigated six cases of enterovirus infection in a neonatal unit. The index patient, a 5-day-old boy, was admitted with aseptic meningitis due to echovirus 30 (E30). Secondary infections with E30 occurred in five babies. Comparison of the complete VP1 sequences showed that the isolates recovered from the index patient and his mother were closely related to those recovered from the five babies with secondary infections, demonstrating a nosocomial transmission of the virus. In the phylogenetic tree reconstructed from the VP1 sequences, the isolates formed a monophyletic cluster related to an E30 strain collected in June 1997 during an outbreak of aseptic meningitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemics of viral meningitis caused by echovirus 6 and 30 in Korea in 2008.Virol J. 2012 Feb 15;9:38. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-38. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22336050 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of echovirus 30-associated outbreak of aseptic meningitis in Guangdong in 2012.Virol J. 2013 Aug 23;10:263. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-263. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 23968330 Free PMC article.
-
Recent outbreak of aseptic meningitis in Italy due to Echovirus 30 and phylogenetic relationship with other European circulating strains.J Clin Virol. 2013 Nov;58(3):579-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2013.08.023. Epub 2013 Aug 31. J Clin Virol. 2013. PMID: 24051044
-
Molecular characterization of echovirus 30-associated outbreak of aseptic meningitis in Korea in 2008.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Mar;20(3):643-9. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20372040
-
Investigating the mechanism of Echovirus 30 cell invasion.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1174410. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1174410. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37485505 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An echovirus type 18 outbreak in a neonatal intensive care unit.Eur J Pediatr. 2008 May;167(5):587-9. doi: 10.1007/s00431-007-0516-x. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Eur J Pediatr. 2008. PMID: 17593390
-
[Epidemiologic characteristics and prevention of viral nosocomial infections].Antibiotiques (Paris). 2009 Feb;11(1):29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.antib.2008.10.001. Epub 2008 Nov 29. Antibiotiques (Paris). 2009. PMID: 32288523 Free PMC article. French.
-
Typing of human enterovirus by partial sequencing of VP2.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Aug;45(8):2370-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00093-07. Epub 2007 May 30. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17537940 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective identification of enteroviruses involved in meningitis in 2006 through direct genotyping in cerebrospinal fluid.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Jan;46(1):87-96. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01020-07. Epub 2007 Oct 31. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 17977989 Free PMC article.
-
Virucidal efficacy of glutaraldehyde against enteroviruses is related to the location of lysine residues in exposed structures of the VP1 capsid protein.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Mar;70(3):1717-22. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.3.1717-1722.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15006797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abzug M J. Perinatal enterovirus infections. In: Rotbart H A, editor. Human enterovirus infections. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press; 1995. pp. 221–238.
-
- Aymard M, Chomel J-J, Lina B, Thouvenot D. Annual report 1997. Lyon, France: National Reference Center for Enteroviruses and Hepatitis A; 1997.
-
- Bailly J-L, Borman A M, Peigue-Lafeuille H, Kean K M. Natural isolates of echovirus type 25 with extensive variations in IRES sequences and different translational efficiencies. Virology. 1996;215:83–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

