The NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway in aortic endothelial cells is primed for activation in regions predisposed to atherosclerotic lesion formation
- PMID: 10922059
- PMCID: PMC16820
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.16.9052
The NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway in aortic endothelial cells is primed for activation in regions predisposed to atherosclerotic lesion formation
Abstract
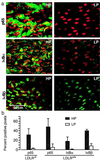
Atherosclerotic lesions form at distinct sites in the arterial tree, suggesting that hemodynamic forces influence the initiation of atherogenesis. If NF-kappaB plays a role in atherogenesis, then the activation of this signal transduction pathway in arterial endothelium should show topographic variation. The expression of NF-kappaB/IkappaB components and NF-kappaB activation was evaluated by specific antibody staining, en face confocal microscopy, and image analysis of endothelium in regions of mouse proximal aorta with high and low probability (HP and LP) for atherosclerotic lesion development. In control C57BL/6 mice, expression levels of p65, IkappaBalpha, and IkappaBbeta were 5- to 18-fold higher in the HP region, yet NF-kappaB was activated in a minority of endothelial cells. This suggested that NF-kappaB signal transduction was primed for activation in HP regions on encountering an activation stimulus. Lipopolysaccharide treatment or feeding low-density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice an atherogenic diet resulted in NF-kappaB activation and up-regulated expression of NF-kappaB-inducible genes predominantly in HP region endothelium. Preferential regional activation of endothelial NF-kappaB by systemic stimuli, including hypercholesterolemia, may contribute to the localization of atherosclerotic lesions at sites with high steady-state expression levels of NF-kappaB/IkappaB components.
Figures


References
-
- Fuster V, Ross R, Topol E J. Atherosclerosis and Coronary Artery Disease. Philadelphia: Lippincott–Raven; 1996.
-
- Ross R. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Munro J M, Cotran R S. Lab Invest. 1988;58:249–261. - PubMed
-
- Ku D N, Zhu C. In: Hemodynamic Forces and Vascular Cell Biology. Sumpio B E, editor. Austin, TX: Landes; 1993. pp. 1–23.
-
- Ishida T, Takahashi M, Corson M A, Berk B C. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1997;811:12–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

