Distinct roles for the yeast phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, Stt4p and Pik1p, in secretion, cell growth, and organelle membrane dynamics
- PMID: 10930462
- PMCID: PMC14948
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.11.8.2673
Distinct roles for the yeast phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, Stt4p and Pik1p, in secretion, cell growth, and organelle membrane dynamics
Abstract
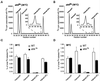
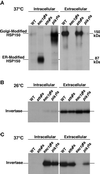
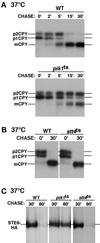
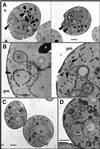
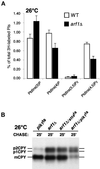
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae possesses two genes that encode phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) 4-kinases, STT4 and PIK1. Both gene products phosphorylate PtdIns at the D-4 position of the inositol ring to generate PtdIns(4)P, which plays an essential role in yeast viability because deletion of either STT4 or PIK1 is lethal. Furthermore, although both enzymes have the same biochemical activity, increased expression of either kinase cannot compensate for the loss of the other, suggesting that these kinases regulate distinct intracellular functions, each of which is required for yeast cell growth. By the construction of temperature-conditional single and double mutants, we have found that Stt4p activity is required for the maintenance of vacuole morphology, cell wall integrity, and actin cytoskeleton organization. In contrast, Pik1p is essential for normal secretion, Golgi and vacuole membrane dynamics, and endocytosis. Strikingly, pik1(ts) cells exhibit a rapid defect in secretion of Golgi-modified secretory pathway cargos, Hsp150p and invertase, whereas stt4(ts) cells exhibit no detectable secretory defects. Both single mutants reduce PtdIns(4)P by approximately 50%; however, stt4(ts)/pik1(ts) double mutant cells produce more than 10-fold less PtdIns(4)P as well as PtdIns(4,5)P(2). The aberrant Golgi morphology found in pik1(ts) mutants is strikingly similar to that found in cells lacking the function of Arf1p, a small GTPase that is known to regulate multiple membrane trafficking events throughout the cell. Consistent with this observation, arf1 mutants exhibit reduced PtdIns(4)P levels. In contrast, diminished levels of PtdIns(4)P observed in stt4(ts) cells at restrictive temperature result in a dramatic change in vacuole size compared with pik1(ts) cells and persistent actin delocalization. Based on these results, we propose that Stt4p and Pik1p act as the major, if not the only, PtdIns 4-kinases in yeast and produce distinct pools of PtdIns(4)P and PtdIns(4,5)P(2) that act on different intracellular membranes to recruit or activate as yet uncharacterized effector proteins.
Figures







References
-
- Bottomley MJ, Salim K, Panayotou G. Phospholipid-binding protein domains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1436:165–183. - PubMed
-
- Conibear E, Stevens TH. Multiple sorting pathways between the late Golgi and the vacuole in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1404:211–230. - PubMed
-
- Cutler NS, Heitman J, Cardenas ME. STT4 is the essential phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase that is a target of wortmannin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:27671–27677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

