Restructuring of focal adhesion plaques by PI 3-kinase. Regulation by PtdIns (3,4,5)-p(3) binding to alpha-actinin
- PMID: 10931873
- PMCID: PMC2175186
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.3.627
Restructuring of focal adhesion plaques by PI 3-kinase. Regulation by PtdIns (3,4,5)-p(3) binding to alpha-actinin
Abstract
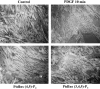
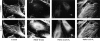
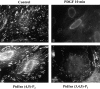
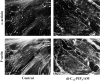
Focal adhesions are an elaborate network of interconnecting proteins linking actin stress fibers to the extracellular matrix substrate. Modulation of the focal adhesion plaque provides a mechanism for the regulation of cellular adhesive strength. Using interference reflection microscopy, we found that activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) by PDGF induces the dissipation of focal adhesions. Loss of this close apposition between the cell membrane and the extracellular matrix coincided with a redistribution of alpha-actinin and vinculin from the focal adhesion complex to the Triton X-100-soluble fraction. In contrast, talin and paxillin remained localized to focal adhesions, suggesting that activation of PI 3-kinase induced a restructuring of the plaque rather than complete dispersion. Furthermore, phosphatidylinositol (3,4, 5)-trisphosphate (PtdIns (3,4,5)-P(3)), a lipid product of PI 3-kinase, was sufficient to induce restructuring of the focal adhesion plaque. We also found that PtdIns (3,4,5)-P(3) binds to alpha-actinin in PDGF-treated cells. Further evidence demonstrated that activation of PI 3-kinase by PDGF induced a decrease in the association of alpha-actinin with the integrin beta subunit, and that PtdIns (3,4,5)-P(3) could disrupt this interaction in vitro. Modification of focal adhesion structure by PI 3-kinase and its lipid product, PtdIns (3,4,5)-P(3), has important implications for the regulation of cellular adhesive strength and motility.
Figures



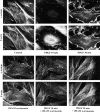

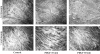

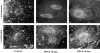
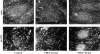







References
-
- Blader I.J., Cope M.J., Jackson T.R., Profit A.A., Greenwood A.F., Drubin D.G., Prestwich G.D., Theibert A.B. GCS1, an arf guanosine triphosphate-activating protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is required for normal actin cytoskeletal organization in vivo and stimulates actin polymerization in vitro. Mol. Biol. Cell. 1999;10:581–596. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blanchard A., Ohanian V., Critchley D. The structure and function of α-actinin. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1989;10:280–289. - PubMed
-
- Bondeva T., Pirola L., Bulgarelli-Leva G., Rubio I., Wetzker R., Wymann M.P. Bifurcation of lipid and protein kinase signals of PI3Kγ to the protein kinases PKB and MAPK. Science. 1998;282:293–296. - PubMed
-
- Burn P., Rotman A., Meyer R.K., Burger M.M. Diacylglycerol in large α-actinin/actin complexes and in the cytoskeleton of activated platelets. Nature. 1985;314:469–474. - PubMed
-
- Burridge K., Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M. Focal adhesions, contractility, and signaling. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996;12:463–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

