The virulence factor AvrXa7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae is a type III secretion pathway-dependent nuclear-localized double-stranded DNA-binding protein
- PMID: 10931960
- PMCID: PMC16946
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.170286897
The virulence factor AvrXa7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae is a type III secretion pathway-dependent nuclear-localized double-stranded DNA-binding protein
Abstract
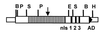
AvrXa7 is a member of the avrBs3 avirulence gene family, which encodes proteins targeted to plant cells by a type III secretion apparatus. AvrXa7, the product of avrXa7, is also a virulence factor in strain PXO86 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Avirulence and virulence specificities are associated with the central repeat domain, which, in avrXa7, consists of 25.5 direct repeat units. Mutations in three C-terminal nuclear localization signal motifs eliminated avirulence and virulence activities in rice and severely reduced nuclear localization in a yeast assay system. Both pathogenicity functions and nuclear localization were restored on the addition of the sequence for the nuclear localization signal motif from SV40 T-antigen. The loss of avirulence activity because of mutations in the acidic transcriptional activation domain was restored by addition of the activation domain from the herpes simplex viral protein VP16. The activation domain was also required for virulence activity. However, the VP16 domain could not substitute for the endogenous domain in virulence assays. In gel shift assays, AvrXa7 bound double-stranded DNA with a preference for dA/dT rich sequences. The results indicate that products of the avrBs3-related genes are virulence factors targeted to host cell nuclei and have the potential to interact with the host DNA and transcriptional machinery as part of their mode of action. The results also suggest that the host defensive recognition mechanisms are targeted to the virulence factor site of action.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Avoidance of host recognition by alterations in the repetitive and C-terminal regions of AvrXa7, a type III effector of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2005 Feb;18(2):142-9. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-18-0142. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2005. PMID: 15720083
-
AvrXa10 contains an acidic transcriptional activation domain in the functionally conserved C terminus.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1998 Aug;11(8):824-32. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.1998.11.8.824. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1998. PMID: 9675896
-
AvrXa7-Xa7 mediated defense in rice can be suppressed by transcriptional activator-like effectors TAL6 and TAL11a from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014 Sep;27(9):983-95. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-09-13-0279-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014. Retraction in: Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014 Dec;27(12):1413. PMID: 25105804 Retracted.
-
Molecular determinants of disease and resistance in interactions of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and rice.Microbes Infect. 2002 Nov;4(13):1361-7. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(02)00004-7. Microbes Infect. 2002. PMID: 12443901 Review.
-
TAL effectors: highly adaptable phytobacterial virulence factors and readily engineered DNA-targeting proteins.Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;23(8):390-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 May 23. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23707478 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TAL effectors: function, structure, engineering and applications.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Feb;23(1):93-9. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Dec 22. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23265998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two type III effector genes of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae control the induction of the host genes OsTFIIAgamma1 and OsTFX1 during bacterial blight of rice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 19;104(25):10720-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701742104. Epub 2007 Jun 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17563377 Free PMC article.
-
The Agrobacterium VirE3 effector protein: a potential plant transcriptional activator.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(22):6496-504. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl877. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 17130174 Free PMC article.
-
TAL effectors and the executor R genes.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Aug 20;6:641. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00641. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26347759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopG1 targets mitochondria, alters plant development and suppresses plant innate immunity.Cell Microbiol. 2010 Mar;12(3):318-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01396.x. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Cell Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19863557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hopkins C M, White F F, Choi S-H, Guo A, Leach J E. Mol Plant–Microbe Interact. 1992;5:451–459. - PubMed
-
- Vivian A, Gibbon M J. Microbiology. 1997;143:693–704. - PubMed
-
- Bonas U, Schulte R, Fenselau S, Minsavage G V, Staskawicz B J, Stall R E. Mol Plant–Microbe Interact. 1991;4:81–88. - PubMed
-
- Bonas U, van den Ackerveken G. Plant J. 1997;12:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

