Proinflammatory cytokine, chemokine, and cellular adhesion molecule expression during the acute phase of experimental brain abscess development
- PMID: 10934167
- PMCID: PMC1850136
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64575-0
Proinflammatory cytokine, chemokine, and cellular adhesion molecule expression during the acute phase of experimental brain abscess development
Abstract
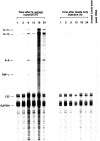
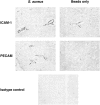
Brain abscess represents the infectious disease sequelae associated with the influx of inflammatory cells and activation of resident parenchymal cells in the central nervous system. However, the immune response leading to the establishment of a brain abscess remains poorly defined. In this study, we have characterized cytokine and chemokine expression in an experimental brain abscess model in the rat during the acute stage of abscess development. RNase protection assay revealed the induction of the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha as early as 1 to 6 hours after Staphylococcus aureus exposure. Evaluation of chemokine expression by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction demonstrated enhanced levels of the CXC chemokine KC 24 hours after bacterial exposure, which correlated with the appearance of neutrophils in the abscess. In addition, two CC chemokines, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha were induced within 24 hours after S. aureus exposure and preceded the influx of macrophages and lymphocytes into the brain. Analysis of abscess lesions by in situ hybridization identified CD11b+ cells as the source of IL-1beta in response to S. aureus. Both intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression were enhanced on microvessels in S. aureus but not sterile bead-implanted tissues at 24 and 48 hours after treatment. These results characterize proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression during the early response to S. aureus in the brain and provide the foundation to assess the functional significance of these mediators in brain abscess pathogenesis.
Figures




References
-
- Wispelwey B, Dacey RG, Scheld WM: Brain abscess. Scheld WM Whitely RJ Durack DT eds. Infections of the Central Nervous System. 1991, :457-486 Raven Press, New York
-
- Mathisen GE, Johnson JP: Brain abscess. Clinical Infect Dis 1997, 25:763-781 - PubMed
-
- Townsend GC, Scheld WM: Infections of the central nervous system. Adv Internal Med 1998, 43:403-447 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Baruch A, Michiel DF, Oppenheim JJ: Signals and receptors involved in recruitment of inflammatory cells. J Biol Chem 1995, 270:11703-11706 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

