Cell-specific transcriptional regulation of human leukotriene B(4) receptor gene
- PMID: 10934229
- PMCID: PMC2193224
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.3.413
Cell-specific transcriptional regulation of human leukotriene B(4) receptor gene
Abstract
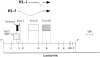
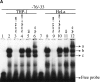
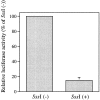
Leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4)) is a lipid mediator that activates leukocytes and is involved in host defense and inflammation. BLT1, a high-affinity receptor for LTB(4) (originally termed BLT), is expressed exclusively in inflammatory cells and is inducible in macrophages upon activation. The mechanisms of tissue-specific expression and induction of BLT1 are important for the understanding of mechanism of onset and the potential treatment of inflammatory disorders. Here, we report the genomic structure and a promoter analysis of the human BLT1 gene, with an emphasis on the mechanism of cell-specific transcription. No TATA or CAAT elements exist around the transcription initiation sites, but a GC-rich sequence is observed in this region. A reporter gene assay revealed that a region approximately 80 basepair upstream from the initiator sequence is required for the basal transcription of the BLT1 gene. Sp1 was found to be a major activator of basal transcription by electrophoretic mobility shift assays and site-directed mutagenesis. The CpG sites of the BLT1 promoter region were highly methylated in BLT1-nonexpressing cells, but not methylated in BLT1-expressing cells. Further, methylation of this region in vitro inhibited the promoter activity to approximately 15% of the control. Thus, methylation at CpG sites in the promoter region is important for cell-specific transcription of the BLT1 gene. The promoter region of the BLT1 gene is localized within the open reading frame (ORF) of the BLT2 gene, which encodes a low-affinity receptor for LTB(4) (Yokomizo, T., K. Kato, K. Terawaki, T. Izumi, and T. Shimizu. 2000. J. Exp. Med. 192:421-431). To our knowledge, this is the first example of "promoter in ORF" in higher eukaryotes.
Figures




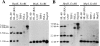
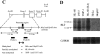
Comment in
-
The scent of a phagocyte: Advances on leukotriene b(4) receptors.J Exp Med. 2000 Aug 7;192(3):F5-8. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.3.f5. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10934235 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ford-Hutchinson A., Doig M.V., Shipley M.E., Smith M.J. Leukotriene B4, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1980;286:264–265. - PubMed
-
- Samuelsson B., Dahlén S.E., Lindgren J.Å., Rouzer C.A., Serhan C.N. Leukotrienes and lipoxinsstructures, biosynthesis, and biological effects. Science. 1987;237:1171–1176. - PubMed
-
- Iversen L., Kragballe K., Ziboh V.A. Significance of leukotriene-A4 hydrolase in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Skin Pharmacol. 1997;10:169–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

