Coactivation of beta-adrenergic and cholinergic receptors enhances the induction of long-term potentiation and synergistically activates mitogen-activated protein kinase in the hippocampal CA1 region
- PMID: 10934239
- PMCID: PMC6772603
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-16-05924.2000
Coactivation of beta-adrenergic and cholinergic receptors enhances the induction of long-term potentiation and synergistically activates mitogen-activated protein kinase in the hippocampal CA1 region
Abstract
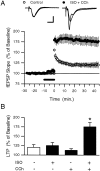
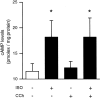
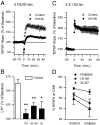
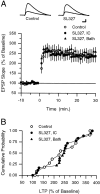
Interactions between noradrenergic and cholinergic receptor signaling may be important in some forms of learning. To investigate whether noradrenergic and cholinergic receptor interactions regulate forms of synaptic plasticity thought to be involved in memory formation, we examined the effects of concurrent beta-adrenergic and cholinergic receptor activation on the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampal CA1 region. Low concentrations of the beta-adrenergic receptor agonist isoproterenol (ISO) and the cholinergic receptor agonist carbachol had no effect on the induction of LTP by a brief train of 5 Hz stimulation when applied individually but dramatically facilitated LTP induction when coapplied. Although carbachol did not enhance ISO-induced increases in cAMP, coapplication of ISO and carbachol synergistically activated p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p42 MAPK). This suggests that concurrent beta-adrenergic and cholinergic receptor activation enhances LTP induction by activating MAPK and not by additive or synergistic effects on adenylyl cyclase. Consistent with this, blocking MAPK activation with MEK inhibitors suppressed the facilitation of LTP induction produced by concurrent beta-adrenergic and cholinergic receptor activation. Although MEK inhibitors also suppressed the induction of LTP by a stronger 5 Hz stimulation protocol that induced LTP in the absence of ISO and carbachol, they had no effect on LTP induced by high-frequency synaptic stimulation or low-frequency synaptic stimulation paired with postsynaptic depolarization. Our results indicate that MAPK activation has an important, modulatory role in the induction of LTP and suggest that coactivation of noradrenergic and cholinergic receptors regulates LTP induction via convergent effects on MAPK.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates early phosphorylation and delayed expression of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in long-term potentiation.J Neurosci. 2001 Sep 15;21(18):7053-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07053.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11549715 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulates the induction of long-term potentiation through extracellular signal-related kinase-independent mechanisms.J Neurosci. 2003 May 1;23(9):3679-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-09-03679.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12736339 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of short-term potentiation to long-term potentiation in mouse CA1 by coactivation of β-adrenergic and muscarinic receptors.Learn Mem. 2012 Oct 17;19(11):535-42. doi: 10.1101/lm.026898.112. Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 23077334
-
Viagra for your synapses: Enhancement of hippocampal long-term potentiation by activation of beta-adrenergic receptors.Cell Signal. 2010 May;22(5):728-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.12.004. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20043991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noradrenergic gating of long-lasting synaptic potentiation in the hippocampus: from neurobiology to translational biomedicine.J Neurogenet. 2018 Sep;32(3):171-182. doi: 10.1080/01677063.2018.1497630. Epub 2018 Sep 3. J Neurogenet. 2018. PMID: 30175650 Review.
Cited by
-
Alzheimer's disease is an inherent, natural part of human brain aging: an integrated perspective.Free Neuropathol. 2022 Jul 8;3:17. doi: 10.17879/freeneuropathology-2022-3806. eCollection 2022 Jan. Free Neuropathol. 2022. PMID: 37284149 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) knockdown mice show deficits in long-term memory; ERK2 has a specific function in learning and memory.J Neurosci. 2007 Oct 3;27(40):10765-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0117-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17913910 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase is required, but not sufficient, for the induction of long-term potentiation in dentate gyrus neurons in vivo.J Neurosci. 2003 May 15;23(10):4072-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-10-04072.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12764094 Free PMC article.
-
SynGAP regulates ERK/MAPK signaling, synaptic plasticity, and learning in the complex with postsynaptic density 95 and NMDA receptor.J Neurosci. 2002 Nov 15;22(22):9721-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-22-09721.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12427827 Free PMC article.
-
A role for ERK MAP kinase in physiologic temporal integration in hippocampal area CA1.Learn Mem. 2003 Jan-Feb;10(1):26-39. doi: 10.1101/lm.51103. Learn Mem. 2003. PMID: 12551961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams JP, Anderson AE, Johnston D, Pfaffinger PJ, Sweatt JD. Kv4.2: a novel substrate for MAP kinase phosphorylation. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1997;23:1176.
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Bading H, Greenberg ME. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by NMDA receptor activation. Science. 1991;253:912–914. - PubMed
-
- Baron C, Benes C, Tan HV, Fagard R, Roisin M-P. Potassium chloride pulse enhances mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurochem. 1996;66:1005–1010. - PubMed
-
- Baumgold J. Muscarinic receptor-mediated stimulation of adenylyl cyclase. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992;13:339–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
