Somatostatin-induced regulation of SST(2A) receptor expression and cellsurface availability in central neurons: role of receptor internalization
- PMID: 10934240
- PMCID: PMC6772591
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-16-05932.2000
Somatostatin-induced regulation of SST(2A) receptor expression and cellsurface availability in central neurons: role of receptor internalization
Abstract
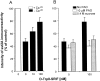
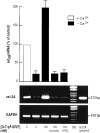
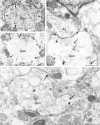
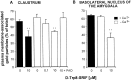
To investigate the effects of somatostatin (somatotropin release-inhibiting factor, SRIF) on the regulation of SST(2A) receptors in mammalian brain, we examined how blockade of SRIF release or stimulation by the SRIF analog [d-Trp(8)]-SRIF would affect the expression and cell surface availability of SST(2A) receptors in rat brain slices. First, we measured the intensity of SST(2A) immunoreactivity, using quantitative light microscopic immunocytochemistry, and levels of SST(2A) mRNA, using semiquantitative RT-PCR, under conditions of acute SRIF release blockade. Incubation of slices from the claustrum or basolateral amygdala, two regions previously shown to contain high concentrations of SST(2A) receptors, in Ca(2+)-free Ringer's for 40 min induced a decrease in the intensity of SST(2A) receptor immunoreactivity and concentration of SST(2A) mRNA as compared with control values obtained in Ca(2+)-supplemented Ringer's. These effects were counteracted in a dose-dependent manner by the addition of 10-100 nm [d-Trp(8)]-SRIF to the Ca(2+)-free medium. Furthermore, both of these effects were abolished in the presence of the endocytosis inhibitors phenylarsine oxide or hyperosmolar sucrose, suggesting that they were dependent on receptor internalization. Electron microscopic immunogold labeling confirmed the existence of an agonist-induced internalization of SST(2A) receptors in central neurons. At a high (10 microm), but not at a low (10 nm), concentration of agonist this internalization resulted in a significant decrease in cell surface receptor density, irrespective of the presence of Ca(2+) in the medium. Taken together, these results suggest that ligand-induced endocytosis is responsible for rapid transcriptional (increase in SST(2A) expression) and trafficking (loss of cell surface receptors) events involved in the control of the somatostatinergic signal.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coexpression of somatostatin receptor subtype 5 affects internalization and trafficking of somatostatin receptor subtype 2.Endocrinology. 2007 May;148(5):2095-105. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1266. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17272399
-
Somatostatin (SRIF) and SRIF receptors in the mouse retina.Brain Res. 2002 May 17;936(1-2):1-14. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)02450-2. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 11988224
-
Receptor-mediated internalization of somatostatin in rat cortical and hippocampal neurons.Synapse. 2000 Nov;38(2):177-86. doi: 10.1002/1098-2396(200011)38:2<177::AID-SYN9>3.0.CO;2-S. Synapse. 2000. PMID: 11018792
-
Somatostatin and somatostatin subtype 2A expression in the mammalian retina.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Jul 15;50(2):103-11. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20000715)50:2<103::AID-JEMT2>3.0.CO;2-X. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10891874 Review.
-
Somatostatin receptor manipulation.Digestion. 1996;57 Suppl 1:7-10. doi: 10.1159/000201383. Digestion. 1996. PMID: 8813458 Review.
Cited by
-
Somatostatin receptor 2 is activated in cortical neurons and contributes to neurodegeneration after focal ischemia.J Neurosci. 2004 Dec 15;24(50):11404-15. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3834-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15601946 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin type-2 receptor activation inhibits glutamate release and prevents status epilepticus.Neurobiol Dis. 2013 Jun;54:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.02.015. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2013. PMID: 23473742 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical distribution and subcellular localization of the somatostatin receptor subtype 1 (sst1) in the rat hypothalamus.Neurochem Res. 2006 Feb;31(2):247-57. doi: 10.1007/s11064-005-9013-7. Epub 2006 Mar 2. Neurochem Res. 2006. PMID: 16518576
-
Agonist-induced internalization of serotonin-1a receptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus (autoreceptors) but not hippocampus (heteroreceptors).J Neurosci. 2001 Nov 1;21(21):8378-86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-21-08378.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11606626 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA-sst2 somatostatin receptor interaction in rat hypothalamus requires activation of NMDA and/or metabotropic glutamate receptors and depends on intracellular calcium.J Physiol. 2003 Jan 1;546(Pt 1):101-17. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.025890. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12509482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaudet A, Greenspun D, Raelson J, Tannenbaum GS. Patterns of expression of SSTR1 and SSTR2 somatostatin receptor subtypes in the hypothalamus of the adult rat: relationship to neuroendocrine function. Neuroscience. 1995;65:551–561. - PubMed
-
- Beaumont V, Hepworth MB, Luty JS, Kelly E, Henderson G. Somatostatin receptor desensitization in NG108-15 cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33174–33183. - PubMed
-
- Bevan AP, Burgess JW, Drake PG, Shaver A, Bergeron JJ, Posner BI. Selective activation of the rat hepatic endosomal insulin receptor kinase. Role for the endosome in insulin signaling. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:10784–10791. - PubMed
-
- Brazeau P, Vale W, Burgus R, Ling N, Butcher M, Rivier J, Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973;179:77–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
