Brassinosteroid-insensitive-1 is a ubiquitously expressed leucine-rich repeat receptor serine/threonine kinase
- PMID: 10938344
- PMCID: PMC59084
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.123.4.1247
Brassinosteroid-insensitive-1 is a ubiquitously expressed leucine-rich repeat receptor serine/threonine kinase
Abstract
Brassinosteroid (BR) mutants of Arabidopsis have pleiotropic phenotypes and provide evidence that BRs function throughout the life of the plant from seedling development to senescence. Screens for BR signaling mutants identified one locus, BRI1, which encodes a protein with homology to leucine-rich repeat receptor serine (Ser)/threonine (Thr) kinases. Twenty-seven alleles of this putative BR receptor have been isolated to date, and we present here the identification of the molecular lesions of 14 recessive alleles that represent five new mutations. BR-insensitive-1 (BRI1) is expressed at high levels in the meristem, root, shoot, and hypocotyl of seedlings and at lower levels later in development. Confocal microscopy analysis of full-length BRI1 fused to green fluorescent protein indicates that BRI1 is localized in the plasma membrane, and an in vitro kinase assay indicates that BRI1 is a functional Ser/Thr kinase. Among the bri1 mutants identified are mutants in the kinase domain, and we demonstrate that one of these mutations severely impairs BRI1 kinase activity. Therefore, we conclude that BRI1 is a ubiquitously expressed leucine-rich repeat receptor that plays a role in BR signaling through Ser/Thr phosphorylation.
Figures
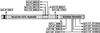
 , Signal peptide;
, Signal peptide;  , putative Leu-zipper motif;
, putative Leu-zipper motif;  , Cys pair;
, Cys pair;  , LRRs;
, LRRs;  , 70-amino acid island;
, 70-amino acid island;  , transmembrane domain;
, transmembrane domain;  , kinase domain. Asterisk, These alleles were published by Noguchi et al. (1999).
, kinase domain. Asterisk, These alleles were published by Noguchi et al. (1999).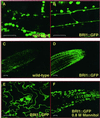

References
-
- Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G. Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot. Cell. 1995;83:851–857. - PubMed
-
- Becraft PW. Receptor kinases in plant development. Trends Plant Sci. 1998;3:384–388.
-
- Boyle WJ, van der Geer P, Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. - PubMed
-
- Braun DM, Stone JM, Walker JC. Interaction of the maize and Arabidopsis kinase interaction domains with a subset of receptor-like protein kinases: implications for transmembrane signaling in plants. Plant J. 1997;12:83–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

