In vivo and in vitro effects of (p)ppGpp on the sigma(54) promoter Pu of the TOL plasmid of Pseudomonas putida
- PMID: 10940009
- PMCID: PMC111345
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.17.4711-4718.2000
In vivo and in vitro effects of (p)ppGpp on the sigma(54) promoter Pu of the TOL plasmid of Pseudomonas putida
Abstract
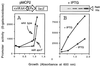
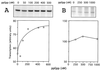
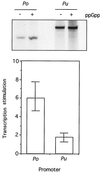
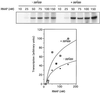
The connection between the physiological control of the sigma(54)-dependent Pu promoter of the TOL plasmid pWW0 of Pseudomonas putida and the stringent response mediated by the alarmone (p)ppGpp has been examined in vivo an in vitro. To this end, the key regulatory elements of the system were faithfully reproduced in an Escherichia coli strain and assayed as lacZ fusions in various genetic backgrounds lacking (p)ppGpp or overexpressing relA. Neither the responsiveness of Pu to 3-methyl benzylalcohol mediated by its cognate activator XylR nor the down-regulation of the promoter by rapid growth were affected in relA/spoT strains to an extent which could account for the known physiological control that governs this promoter. Overexpression of the relA gene [predicted to increase intracellullar (p)ppGpp levels] did, however, cause a significant gain in Pu activity. Since such a gain might be the result of indirect effects, we resorted to an in vitro transcription system to assay directly the effect of ppGpp on the transcriptional machinery. Although we did observe a significant increase in Pu performance through a range of sigma(54)-RNAP concentrations, such an increase never exceeded twofold. The difference between these results and the behavior of the related Po promoter of the phenol degradation plasmid pVI150 could be traced to the different promoter sequences, which may dictate the type of metabolic signals recruited for the physiological control of sigma(54)-systems.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The alarmone (p)ppGpp mediates physiological-responsive control at the sigma 54-dependent Po promoter.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Feb;31(4):1217-28. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01264.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10096088
-
Transcriptional wiring of the TOL plasmid regulatory network to its host involves the submission of the sigma54-promoter Pu to the response regulator PprA.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Aug;69(3):698-713. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06321.x. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 19138193
-
Genetic evidence of distinct physiological regulation mechanisms in the sigma(54) Pu promoter of Pseudomonas putida.J Bacteriol. 2000 Feb;182(4):956-60. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.4.956-960.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10648520 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional control of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid catabolic operons is achieved through an interplay of host factors and plasmid-encoded regulators.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1997;51:341-73. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.51.1.341. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9343354 Review.
-
Transcriptional control of the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid catabolic pathways.Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(5):923-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01222.x. Mol Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 7934920 Review.
Cited by
-
An active role for a structured B-linker in effector control of the sigma54-dependent regulator DmpR.EMBO J. 2001 Feb 15;20(4):819-27. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.4.819. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11179226 Free PMC article.
-
The black cat/white cat principle of signal integration in bacterial promoters.EMBO J. 2001 Jan 15;20(1-2):1-11. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.1.1. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11226149 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Integration of global regulation of two aromatic-responsive sigma(54)-dependent systems: a common phenotype by different mechanisms.J Bacteriol. 2002 Feb;184(3):760-70. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.3.760-770.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 11790746 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo and in vitro effects of integration host factor at the DmpR-regulated sigma(54)-dependent Po promoter.J Bacteriol. 2001 May;183(9):2842-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.9.2842-2851.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11292804 Free PMC article.
-
Protective action of ppGpp in microcin J25-sensitive strains.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jun;190(12):4328-34. doi: 10.1128/JB.00183-08. Epub 2008 Apr 11. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18408024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aviv M, Giladi H, Schreiber G, Oppenheim A B, Glaser G. Expression of the genes coding for the Escherichia coli integration host factor are controlled by growth phase, rpoS, ppGpp and by autoregulation. Mol Microbiol. 1994;14:1021–1031. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett M S, Gaal T, Ross W, Gourse R L. RNA polymerase mutants that destabilize RNA polymerase-promoter complexes alter NTP-sensing by rrn P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1998;279:331–345. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

