RNase III processing of intervening sequences found in helix 9 of 23S rRNA in the alpha subclass of Proteobacteria
- PMID: 10940010
- PMCID: PMC111346
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.17.4719-4729.2000
RNase III processing of intervening sequences found in helix 9 of 23S rRNA in the alpha subclass of Proteobacteria
Abstract
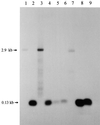
We provide experimental evidence for RNase III-dependent processing in helix 9 of the 23S rRNA as a general feature of many species in the alpha subclass of Proteobacteria (alpha-Proteobacteria). We investigated 12 Rhodobacter, Rhizobium, Sinorhizobium, Rhodopseudomonas, and Bartonella strains. The processed region is characterized by the presence of intervening sequences (IVSs). The 23S rDNA sequences between positions 109 and 205 (Escherichia coli numbering) were determined, and potential secondary structures are proposed. Comparison of the IVSs indicates very different evolutionary rates in some phylogenetic branches, lateral genetic transfer, and evolution by insertion and/or deletion. We show that the IVS processing in Rhodobacter capsulatus in vivo is RNase III-dependent and that RNase III cleaves additional sites in vitro. While all IVS-containing transcripts tested are processed in vitro by RNase III from R. capsulatus, E. coli RNase III recognizes only some of them as substrates and in these substrates frequently cleaves at different scissile bonds. These results demonstrate the different substrate specificities of the two enzymes. Although RNase III plays an important role in the rRNA, mRNA, and bacteriophage RNA maturation, its substrate specificity is still not well understood. Comparison of the IVSs of helix 9 does not hint at sequence motives involved in recognition but reveals that the "antideterminant" model, which represents the most recent attempt to explain the E. coli RNase III specificity in vitro, cannot be applied to substrates derived from alpha-Proteobacteria.
Figures
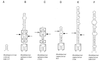
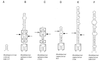
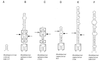


References
-
- Amarger N, Macheret V, Laguerre G. Rhizobium gallicum sp. nov. and Rhizobium giardinii sp. nov., from Phaseolus vulgaris nodules. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1997;47:996–1006. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. I. New York, N.Y: Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience; 1989.
-
- Beringer J E. R-factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974;84:188–198. - PubMed
-
- Burgin A B, Parodos K, Lane D J, Pace N R. The excision of intervening sequences from Salmonella 23S ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1990;60:405–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

