dMi-2 and ISWI chromatin remodelling factors have distinct nucleosome binding and mobilization properties
- PMID: 10944116
- PMCID: PMC302042
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.16.4332
dMi-2 and ISWI chromatin remodelling factors have distinct nucleosome binding and mobilization properties
Abstract
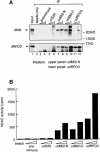
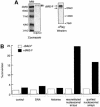
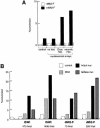
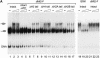
Mi-2 and ISWI, two members of the Snf2 superfamily of ATPases, reside in separate ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling complexes. These complexes differ in their biochemical properties and are believed to perform distinct functions in the cell. We have compared the remodelling activity of recombinant Drosophila Mi-2 (dMi-2) with that of recombinant ISWI. Both proteins are nucleosome-stimulated ATPases and promote nucleosome mobilization. However, dMi-2 and ISWI differ in their interaction with nucleosome core particles, in their substrate requirements and in the direction of nucleosome mobilization. We have used antibodies to immobilize a complex containing dMi-2 and the dRPD3 histone deacetylase from Drosophila embryo extracts. This complex shares the nucleosome-stimulated ATPase and nucleosome mobilization properties of recombinant dMi-2, demonstrating that these activities are maintained in a physiological context. Its functional properties distinguish dMi-2 from both SWI2/SNF2 and ISWI, defining a new family of ATP-dependent remodelling machines.
Figures

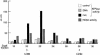

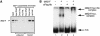
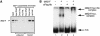

References
-
- Akthar A. and Becker,P.B. (2000) Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell, 5, 1–9. - PubMed
-
- Brehm A., Miska,E.A., McCance,D.J., Reid,J.L., Bannister,A.J. and Kouzarides,T. (1998) Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription. Nature, 391, 597–601. - PubMed
-
- Cairns B.R. (1998) Chromatin remodeling machines: similar motors, ulterior motives. Trends Biochem. Sci., 23, 20–25. - PubMed
-
- Corona D.F., Langst,G., Clapier,C.R., Bonte,E.J., Ferrari,S., Tamkun,J.W. and Becker,P.B. (1999) ISWI is an ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling factor. Mol. Cell, 3, 239–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

