Diminished function and expression of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger in diabetic rats: implication in Ca2+ overload
- PMID: 10944172
- PMCID: PMC2270056
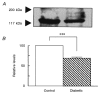
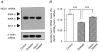
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00085.x
Diminished function and expression of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger in diabetic rats: implication in Ca2+ overload
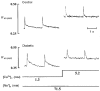
Abstract
1. The present work was carried out in order to determine whether a decrease in cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) activity observed in diabetes is caused by a reduction in NCX protein and mRNA levels and to elucidate the significance of this decrease in alterations in [Ca2+]i homeostasis in diabetic cardiomyocytes. 2. The NCX current was significantly reduced in ventricular myocytes freshly isolated from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat hearts, and its current density was about 55 % of age-matched controls. 3. Diabetes resulted in a 30 % decrease in cardiac protein and mRNA levels of NCX1, a NCX isoform which is expressed at high levels in the heart. 4. The reduced NCX current and the decreased protein and mRNA levels of NCX1 in diabetes were prevented by insulin therapy. 5. Although both diastolic and peak systolic [Ca2+]i were not different between the two groups of myocytes, increasing external Ca2+ concentration to high levels greatly elevated diastolic [Ca2+]i in diabetic myocytes. Inhibition of NCX by reduction in extracellular Na+ by 50 % could produce a marked rise in diastolic [Ca2+]i in control myocytes in response to high Ca2+, as seen in diabetic myocytes. However, cyclopiazonic acid, an inhibitor of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump ATPase, did not modify the high Ca2+-induced changes in diastolic [Ca2+]i in either control or diabetic myocytes. 6. Only in papillary muscles from diabetic rats did the addition of high Ca2+ cause a marked rise in resting tension signifying a partial contracture that was possibly due to an increase in diastolic [Ca2+]i. 7. In conclusion, the diminished NCX function in diabetic myocytes shown in this study results in part from the decreased levels of cardiac NCX protein and mRNA. We suggest that this impaired NCX function may play an important role in alterations in Ca2+ handling when [Ca2+]i rises to pathological levels.
Figures


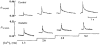
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms underlying depressed Na+/Ca2+ exchanger activity in the diabetic heart.Cardiovasc Res. 1997 Apr;34(1):129-36. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(97)00020-5. Cardiovasc Res. 1997. PMID: 9217882
-
Endothelin-1 stimulates the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger reverse mode through intracellular Na+ (Na+i)-dependent and Na+i-independent pathways.Hypertension. 2005 Feb;45(2):288-93. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000152700.58940.b2. Epub 2004 Dec 20. Hypertension. 2005. PMID: 15611361
-
Propofol modulates Na+-Ca2+ exchange activity via activation of protein kinase C in diabetic cardiomyocytes.Anesthesiology. 2007 Feb;106(2):302-11. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200702000-00019. Anesthesiology. 2007. PMID: 17264725
-
Genetic manipulation of cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchange expression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Oct 1;322(4):1336-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.038. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 15336980 Review.
-
Cardiac sodium-calcium exchange and efficient excitation-contraction coupling: implications for heart disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:355-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_30. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
O-linked GlcNAc modification of cardiac myofilament proteins: a novel regulator of myocardial contractile function.Circ Res. 2008 Dec 5;103(12):1354-8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.184978. Epub 2008 Nov 6. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18988896 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of insulin on altered mechanical and electrical papillary muscle activities of diabetic rats.J Membr Biol. 2013 Jan;246(1):31-7. doi: 10.1007/s00232-012-9499-2. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Membr Biol. 2013. PMID: 22968850
-
The interplay of inflammation, exosomes and Ca2+ dynamics in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Feb 20;22(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01755-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 36804872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Signaling in the Ventricular Myocardium of the Goto-Kakizaki Type 2 Diabetic Rat.J Diabetes Res. 2018 Apr 10;2018:2974304. doi: 10.1155/2018/2974304. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 29850600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase activity is unchanged despite increased myofilament calcium sensitivity in Zucker type 2 diabetic fatty rat heart.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 7;12(1):16904. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20520-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36207382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barry WH, Bridge JHB. Intracellular calcium homeostasis in cardiac myocytes. Circulation. 1993;87:1806–1815. - PubMed
-
- Callewaert G. Excitation-contraction coupling in mammalian cardiac cells. Cardiovascular Research. 1992;26:923–932. - PubMed
-
- Chomczinski P, Sacchi N. Single step method of RNA isolation by guanidine thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Analytical Biochemistry. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
-
- Dhalla NS, Pierce GN, Innes IR, Beamish RE. Pathogenesis of cardiac dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 1985;1:263–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

