Ions, cell volume, and apoptosis
- PMID: 10944207
- PMCID: PMC34029
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.17.9360
Ions, cell volume, and apoptosis
Figures
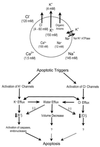
Comment on
-
Normotonic cell shrinkage because of disordered volume regulation is an early prerequisite to apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 15;97(17):9487-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.140216197. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10900263 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

