Structure-based design of an osteoclast-selective, nonpeptide src homology 2 inhibitor with in vivo antiresorptive activity
- PMID: 10944210
- PMCID: PMC16871
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.17.9373
Structure-based design of an osteoclast-selective, nonpeptide src homology 2 inhibitor with in vivo antiresorptive activity
Abstract
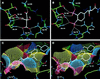
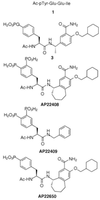
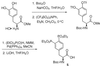
Targeted disruption of the pp60(src) (Src) gene has implicated this tyrosine kinase in osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and as a therapeutic target for the treatment of osteoporosis and other bone-related diseases. Herein we describe the discovery of a nonpeptide inhibitor (AP22408) of Src that demonstrates in vivo antiresorptive activity. Based on a cocrystal structure of the noncatalytic Src homology 2 (SH2) domain of Src complexed with citrate [in the phosphotyrosine (pTyr) binding pocket], we designed 3',4'-diphosphonophenylalanine (Dpp) as a pTyr mimic. In addition to its design to bind Src SH2, the Dpp moiety exhibits bone-targeting properties that confer osteoclast selectivity, hence minimizing possible undesired effects on other cells that have Src-dependent activities. The chemical structure AP22408 also illustrates a bicyclic template to replace the post-pTyr sequence of cognate Src SH2 phosphopeptides such as Ac-pTyr-Glu-Glu-Ile (1). An x-ray structure of AP22408 complexed with Lck (S164C) SH2 confirmed molecular interactions of both the Dpp and bicyclic template of AP22408 as predicted from molecular modeling. Relative to the cognate phosphopeptide, AP22408 exhibits significantly increased Src SH2 binding affinity (IC(50) = 0.30 microM for AP22408 and 5.5 microM for 1). Furthermore, AP22408 inhibits rabbit osteoclast-mediated resorption of dentine in a cellular assay, exhibits bone-targeting properties based on a hydroxyapatite adsorption assay, and demonstrates in vivo antiresorptive activity in a parathyroid hormone-induced rat model.
Figures
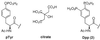


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

