Extract of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis stimulates polyclonal type-2 immunoglobulin response by inducing De novo class switch
- PMID: 10948105
- PMCID: PMC101699
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.4913-4922.2000
Extract of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis stimulates polyclonal type-2 immunoglobulin response by inducing De novo class switch
Abstract
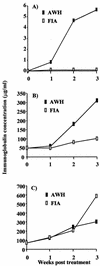
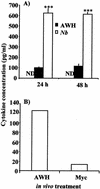
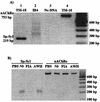
Infection with the nematode parasite Nippostrongylus brasiliensis induces a pronounced type-2 T-cell response that is associated with marked polyclonal immunoglobulin E (IgE) and IgG1 production in mice. To examine the differential roles of the infection and products produced by nematodes, we investigated a soluble extract of N. brasiliensis for the ability to mediate this type-2 response. We found that the extract induced a marked increase in IgE and IgG1 levels, similar to that induced by the infection. The extract did not affect the level of IgG2a in serum, showing that the effect was specific to IgE and IgG1 (type-2-associated immunoglobulin) rather than inducing a nonspecific increase in all immunoglobulin isotypes. This response was also associated with increased interleukin-4 production in vitro. These results confirm that the extract, like infection, is a strong inducer of polyclonal type-2 responses and a reliable model for investigating the regulation of nematode-induced responses. The extract induced the production of IgG1 when added to in vitro cultures of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated B cells. This provides evidence for the induction of class switch. It did not induce upregulation of IgG1 in naive (unstimulated) B cells or expand B cells in in vitro cultures. Analysis of DNA from the spleens of mice treated with the extract by digestion-circularization PCR demonstrated a marked increase in the occurrence of gamma1 switch region gene recombination in the cells in vivo. These results provide strong evidence that soluble worm products are able to mediate the marked polyclonal gamma1/epsilon response and that infection is not required to mediate this response. Furthermore, these data provide evidence that the soluble nematode extract induces this effect by causing de novo class switch of B cells and not by an expansion of IgG1 B cells or an increase in antibody production by IgG1 plasma cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
IL-2 inhibits IL-4-dependent IgE and IgG1 production in vitro and in vivo.Int Immunol. 1995 Feb;7(2):259-68. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.2.259. Int Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7734421
-
Concomitant immunoglobulin E and immunoglobulin G1 formation in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis-infected mice.J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1459-65. J Immunol. 1987. PMID: 3624863
-
IgE and IgG2a antibody responses are induced by different antigen groups of the nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in rats.Immunology. 1993 Feb;78(2):298-302. Immunology. 1993. PMID: 8473018 Free PMC article.
-
The IgE and IgG subclass responses of mice to four helminth parasites.Cell Immunol. 1989 Mar;119(1):193-201. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90235-9. Cell Immunol. 1989. PMID: 2522026
-
One cytokine, two isotypes: a trojan horse, pandora's box, and an evolving paradigm.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Sep;162(3 Pt 2):S86-90. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.162.supplement_2.ras-6. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. PMID: 10988158 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Elevated immunoglobulin E against recombinant Brugia malayi gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in patients with bancroftian filariasis: association with tropical pulmonary eosinophilia or putative immunity.Infect Immun. 2003 Feb;71(2):747-53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.747-753.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12540554 Free PMC article.
-
Class switching is differentially regulated in RBC alloimmunization and vaccination.Transfusion. 2023 Apr;63(4):826-838. doi: 10.1111/trf.17301. Epub 2023 Mar 12. Transfusion. 2023. PMID: 36907655 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of a heterologous immune response by the products of Ascaris suum.Infect Immun. 2002 Nov;70(11):6058-67. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.11.6058-6067.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12379682 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted proteomes of different developmental stages of the gastrointestinal nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Oct;13(10):2736-51. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.038950. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24994561 Free PMC article.
-
A 24 kDa excretory-secretory protein of Anisakis simplex larvae could elicit allergic airway inflammation in mice.Korean J Parasitol. 2011 Dec;49(4):373-80. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2011.49.4.373. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Korean J Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 22355204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bancroft A J, Grencis R K. Th1 and Th2 cells and immunity to intestinal helminths. Chem Immunol. 1998;71:192–208. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft A J, McKenzie A N J, Grencis R K. A critical role for IL-13 in resistance to intestinal nematode infection. J Immunol. 1998;160:3453–3461. - PubMed
-
- Barner M, Mohrs M, Brombacher F, Kopf M. Differences between IL-4Rα-deficient and IL-4-deficient mice reveal a role for IL-13 in the regulation of Th2 responses. Curr Biol. 1998;8:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Beck L, Spiegelberg H L. The polyclonal and antigen-specific IgE, IgG1 and IgG2a response of mice injected with ovalbumin in alum or complete freund's adjuvant. Cell Immunol. 1989;123:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

