Serum amyloid P component prevents high-density lipoprotein-mediated neutralization of lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 10948110
- PMCID: PMC101709
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.4954-4960.2000
Serum amyloid P component prevents high-density lipoprotein-mediated neutralization of lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
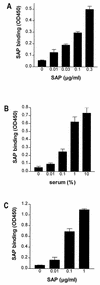
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an amphipathic macromolecule that is highly aggregated in aqueous preparations. LPS-binding protein (LBP) catalyzes the transfer of single LPS molecules, segregated from an LPS aggregate, to high-density lipoproteins (HDL), which results in the neutralization of LPS. When fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled LPS (FITC-LPS) is used, this transfer of LPS monomers to HDL can be measured as an increase in fluorescence due to dequenching of FITC-LPS. Recently, serum amyloid P component (SAP) was shown to neutralize LPS in vitro, although only in the presence of low concentrations of LBP. In this study, we show that SAP prevented HDL-mediated dequenching of FITC-LPS, even in the presence of high concentrations of LBP. Human bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI), a very potent LPS-binding and -neutralizing protein, also prevented HDL-mediated dequenching of FITC-LPS. Furthermore, SAP inhibited HDL-mediated neutralization of both rough and smooth LPS in a chemiluminescence assay quantifying the LPS-induced priming of neutrophils in human blood. SAP bound both isolated HDL and HDL in serum. Using HDL-coated magnetic beads prebound with SAP, we demonstrated that HDL-bound SAP prevented the binding of LPS to HDL. We suggest that SAP, by preventing LPS binding to HDL, plays a regulatory role, balancing the amount of LPS that, via HDL, is directed to the adrenal glands.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Analysis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding characteristics of serum components using gel filtration of FITC-labeled LPS.J Immunol Methods. 2000 Aug 28;242(1-2):79-89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(00)00207-6. J Immunol Methods. 2000. PMID: 10986391
-
A synthetic lipopolysaccharide-binding peptide based on amino acids 27-39 of serum amyloid P component inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced responses in human blood.J Immunol. 1998 Oct 1;161(7):3607-15. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9759883
-
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein is carried on lipoproteins and acts as a cofactor in the neutralization of LPS.J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):1025-35. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.1025. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 8064223 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of serum amyloid P component, a novel lipopolysaccharide-binding protein.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999 Dec;26(3-4):197-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1999.tb01390.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10575130 Review.
-
The role of gut-derived oxidized lipids and bacterial lipopolysaccharide in systemic inflammation and atherosclerosis.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2022 Oct 1;33(5):277-282. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000841. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2022. PMID: 35979993 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Receptors, mediators, and mechanisms involved in bacterial sepsis and septic shock.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003 Jul;16(3):379-414. doi: 10.1128/CMR.16.3.379-414.2003. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12857774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of tumour necrosis factor in the kinetics of lipopolysaccharide-mediated neutrophil priming in whole blood.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Apr;140(1):65-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02748.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15762876 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of fibrin clot-bound plasma proteins.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041966. Epub 2012 Aug 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22870270 Free PMC article.
-
Serum amyloid P (SAP) is associated with impaired brachial artery flow-mediated dilation in chronically HIV-1 infected adults on stable antiretroviral therapy.HIV Clin Trials. 2015 Nov;16(6):228-35. doi: 10.1179/1945577115Y.0000000007. HIV Clin Trials. 2015. PMID: 26777795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Haas C J C, Haas P-J, Van Kessel K P M, Van Strijp J A G. Affinities of different proteins and peptides for lipopolysaccharide (LPS) as determined by biosensor technology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;252:492–496. - PubMed
-
- de Haas C J C, Van der Tol M E, Van Kessel K P M, Verhoef J, Van Strijp J A G. A synthetic lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding peptide based on amino acids 27–39 of serum amyloid P component inhibits LPS-induced responses in human blood. J Immunol. 1998;161:3607–3615. - PubMed
-
- de Haas, C. J. C., H. J. van Leeuwen, J. Verhoef, K. P. M. Van Kessel, and J. A. G. Van Strijp. Analysis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding characteristics of serum components using gel filtration of FITC-labeled LPS. J. Immunol. Methods, in press. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

