Serum amyloid P component prevents high-density lipoprotein-mediated neutralization of lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 10948110
- PMCID: PMC101709
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.4954-4960.2000
Serum amyloid P component prevents high-density lipoprotein-mediated neutralization of lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
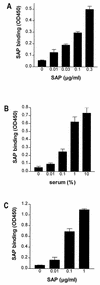
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an amphipathic macromolecule that is highly aggregated in aqueous preparations. LPS-binding protein (LBP) catalyzes the transfer of single LPS molecules, segregated from an LPS aggregate, to high-density lipoproteins (HDL), which results in the neutralization of LPS. When fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled LPS (FITC-LPS) is used, this transfer of LPS monomers to HDL can be measured as an increase in fluorescence due to dequenching of FITC-LPS. Recently, serum amyloid P component (SAP) was shown to neutralize LPS in vitro, although only in the presence of low concentrations of LBP. In this study, we show that SAP prevented HDL-mediated dequenching of FITC-LPS, even in the presence of high concentrations of LBP. Human bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI), a very potent LPS-binding and -neutralizing protein, also prevented HDL-mediated dequenching of FITC-LPS. Furthermore, SAP inhibited HDL-mediated neutralization of both rough and smooth LPS in a chemiluminescence assay quantifying the LPS-induced priming of neutrophils in human blood. SAP bound both isolated HDL and HDL in serum. Using HDL-coated magnetic beads prebound with SAP, we demonstrated that HDL-bound SAP prevented the binding of LPS to HDL. We suggest that SAP, by preventing LPS binding to HDL, plays a regulatory role, balancing the amount of LPS that, via HDL, is directed to the adrenal glands.
Figures



References
-
- de Haas C J C, Haas P-J, Van Kessel K P M, Van Strijp J A G. Affinities of different proteins and peptides for lipopolysaccharide (LPS) as determined by biosensor technology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;252:492–496. - PubMed
-
- de Haas C J C, Van der Tol M E, Van Kessel K P M, Verhoef J, Van Strijp J A G. A synthetic lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding peptide based on amino acids 27–39 of serum amyloid P component inhibits LPS-induced responses in human blood. J Immunol. 1998;161:3607–3615. - PubMed
-
- de Haas, C. J. C., H. J. van Leeuwen, J. Verhoef, K. P. M. Van Kessel, and J. A. G. Van Strijp. Analysis of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding characteristics of serum components using gel filtration of FITC-labeled LPS. J. Immunol. Methods, in press. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

