Presence of phosphorylcholine on a filarial nematode protein influences immunoglobulin G subclass response to the molecule by an interleukin-10-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 10948186
- PMCID: PMC101820
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.5466-5468.2000
Presence of phosphorylcholine on a filarial nematode protein influences immunoglobulin G subclass response to the molecule by an interleukin-10-dependent mechanism
Abstract
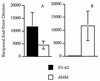
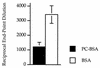
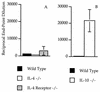
The filarial nematode product ES-62 contains phosphorylcholine (PC) covalently attached to N-linked glycans. ES-62 induced high levels of immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibodies, but no IgG2a, to non-PC epitopes of the molecule following subcutaneous injection into BALB/c mice. Conversely, mice given ES-62 lacking PC demonstrated significant production of both IgG subclasses. Thus, PC appears to block production of IgG2a antibodies to other epitopes on the parasite molecule. A role for interleukin-10 (IL-10) in this effect was shown by the ability of IL-10(-/-) mice to make an IgG2a antibody response to non-PC epitopes of ES-62.
Figures
References
-
- Bach M A, Kowler H, Levitt D. Binding of phosphorylcholine by non-immunoglobulin molecules on mouse B cells. J Immunol. 1983;131:365–369. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C, Paik J, Vodovotz Y, Nathan C. Contrasting mechanisms for suppression of macrophage cytokine release by transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin 10. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:23301–23308. - PubMed
-
- Brewer J M, Roberts C W, Conacher M, McColl J, Blaney B A, Alexander J. An adjuvant formulation that preferentially induces T helper cell type 1 cytokine and CD8+ cytotoxic responses is associated with up-regulation of IL-12 and suppression of IL-10 production. Vaccine Res. 1996;5:77–89.
-
- Callard R E, Matthews D J, Hibbert L. IL-4 and IL-13 receptors: are they one and the same? Immunol Today. 1996;17:108–110. - PubMed
-
- Cooper P J, Espinel I, Paredes W, Guderian R H, Nutman T B. Impaired tetanus-specific cellular and humoral responses following tetanus vaccination in human onchocerciasis: a possible role for interleukin-10. J Infect Dis. 1998;178:1133–1138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

