Quantitative measurements of cerebral blood oxygen saturation using magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 10950383
- PMCID: PMC4096835
- DOI: 10.1097/00004647-200008000-00008
Quantitative measurements of cerebral blood oxygen saturation using magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
A quantitative estimate of cerebral blood oxygen saturation is of critical importance in the investigation of cerebrovascular disease because of the fact that it could potentially provide information on tissue viability in vivo. In the current study, a multi-echo gradient and spin echo magnetic resonance imaging sequence was used to acquire images from eight normal volunteer subjects. All images were acquired on a Siemens 1.5T Symphony whole-body scanner (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). A theoretical signal model, which describes the signal dephasing phenomena in the presence of deoxyhemoglobin, was used for postprocessing of the acquired images and obtaining a quantitative measurement of cerebral blood oxygen saturation in vivo. With a region-of-interest analysis, a mean cerebral blood oxygen saturation of 58.4%+/-1.8% was obtained in the brain parenchyma from all volunteers. It is in excellent agreement with the known cerebral blood oxygen saturation under normal physiologic conditions in humans. Although further studies are needed to overcome some of the confounding factors affecting the estimates of cerebral blood oxygen saturation, these preliminary results are encouraging and should open a new avenue for the noninvasive investigation of cerebral oxygen metabolism under different pathophysiologic conditions using a magnetic resonance imaging approach.
Figures

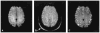

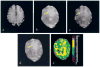
References
-
- Aroner HJ, Gazit IE, Louis DN, et al. Cerebral blood volume maps of gliomas: comparison with tumor grade and histologic findings. Radiology. 1994;191:41–51. - PubMed
-
- Boxerman JL, Hamberg LM, Rosen BR, Weiskoff RM. MR Contrast Due to Intravascular Magnetic Susceptibility Perturbations. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:555–566. - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E, Isselbacher KJ, Petersdorf RG, Wilson JD, Martin JB, Fauci AS. Harrison’s principles of internal medicine. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Book Company; 1987.
-
- Brooks DJ, Beaney RP, Leenden KL, Marshall J, Thomas DJ, Jones T. Regional cerebral oxygen utilization, blood flow and blood volume in benign intracranial hypertension studied by PET. Neurology. 1985;35:1030–1034. - PubMed
-
- Bullock R, Stewart L, Rafferty C, Teasdale GM. Continuous monitoring of jugular bulb oxygen saturation and the effect of drugs acting on cerebral metabolism. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wein) 1993;59:113–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

