The Dlk1 and Gtl2 genes are linked and reciprocally imprinted
- PMID: 10950864
- PMCID: PMC316857
The Dlk1 and Gtl2 genes are linked and reciprocally imprinted
Abstract
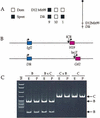
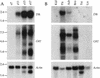
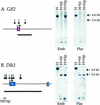
Genes subject to genomic imprinting exist in large chromosomal domains, probably reflecting coordinate regulation of the genes within a cluster. Such regulation has been demonstrated for the H19, Igf2, and Ins2 genes that share a bifunctional imprinting control region. We have identified the Dlk1 gene as a new imprinted gene that is paternally expressed. Furthermore, we show that Dlk1 is tightly linked to the maternally expressed Gtl2 gene. Dlk1 and Gtl2 are coexpressed and respond in a reciprocal manner to loss of DNA methylation. These genes are likely to represent a new example of coordinated imprinting of linked genes.
Figures


References
-
- Bachmann E, Krogh TN, Hojrup P, Skjodt K, Teisner B. Mouse fetal antigen 1 (mFA1), the circulating gene product of mdlk, pref-1 and SCP-1: Isolation, characterization and biology. J Reprod Fertil. 1996;107:279–285. - PubMed
-
- Barlow DP, Stoger R, Herrmann BG, Saito K, Schweifer N. The mouse insulin-like growth factor type-2 receptor is imprinted and closely linked to the Tme locus. Nature. 1991;349:84–87. - PubMed
-
- Bauer SR, Ruiz-Hidalgo MJ, Rudikoff EK, Goldstein J, Laborda J. Modulated expression of the epidermal growth factor-like homeotic protein dlk influences stromal-cell-pre-B-cell interactions, stromal cell adipogenesis, and pre-B-cell interleukin-7 requirements. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:5247–5255. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bell AC, Felsenfeld G. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature. 2000;405:482–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
